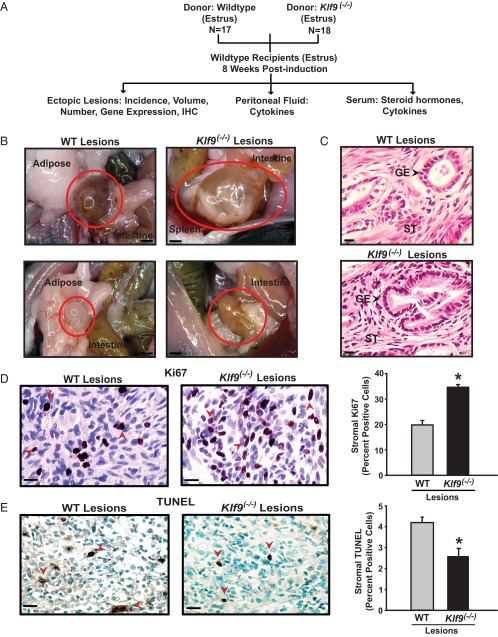
Figure 2.
Experimental design and characterization of endometrial-like lesions in a mouse model of endometriosis. A, Schematic representation of endometrial ectopic lesion generation and their analyses. Klf9 WT mice were used as recipients of endometrial fragments from WT and Klf9−/− null mice (donors) following previously published procedures (38, 39). N is the number of mice used for each experimental paradigm.. B, Representative images of ectopic lesions isolated from WT recipients 8 weeks after ip administration of WT or Klf9 null endometrium. Scale bar corresponds to 1 mm. C, H&E-stained sections of representative WT or Klf9−/− lesions at ×400 magnification. Scale bar corresponds to 20 μm. GE, glandular epithelium; ST, stroma. D, Representative pictures of immunostained stromal cells of WT and Klf9−/− ectopic lesions for proliferation marker Ki67. E, Representative pictures of immunostained stromal cells of WT and Klf9−/− ectopic lesions for apoptotic status (TUNEL). For D and E, the percentage of staining cells (expressed as means ± SEM) was determined by counting the number of immunopositive nuclei over the total number of stromal cells per field. Red arrows demonstrate Ki67-positive (D) and TUNEL-staining (E) stromal cells. Three to four lesions per genotype were analyzed. Scale bar corresponds to 20 μm. *, P < .05 by the Student t test.