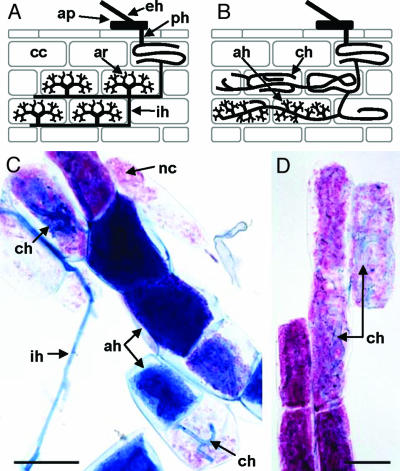
Fig. 2.
StPT3 promoter activity in AM symbioses. (A and B) Features of Arum and Paris types, respectively, of AM. Hyphae of extraradical mycelium (eh) make contact with the host root by forming appressoria (ap) on the root surface. Appressorium-borne hyphae penetrate (ph) the root and give rise to the intraradical mycelium, which in different plant–AMF associations forms two main morphological types, i.e., Arum and Paris. In Arum-type AM (A), intercellular hyphae (ih) grow between the cortical cells (cc) and form fine heavily branched arbuscules (ar) within cortex cells. In Paris-type AM (B), thick coiled hyphae (ch) spread intracellularly. In some cortical cells, lateral branches of coiled hyphae develop into fine branched arbuscule-like structures forming arbusculate hyphae (ah). Intermediate type AM combines features of Arum and Paris types. (C and D) Isolated cortex cells of potato hairy roots harboring the StPT3 promoter-GUS reporter chimeric gene colonized by G. caledonium (C) and G. margarita (D) histochemically stained for GUS activity and fungal mycelium. Magenta staining indicates GUS activity, and AMF hyphae are stained blue. The StPT3 promoter is expressed in cells colonized by both fine branched arbusculate hyphae (ah) and thick-coiled hyphae (ch). GUS products can diffuse into neighboring noncolonized cells (nc); ih, intercellular hypha. (Bars, 50 μm.)