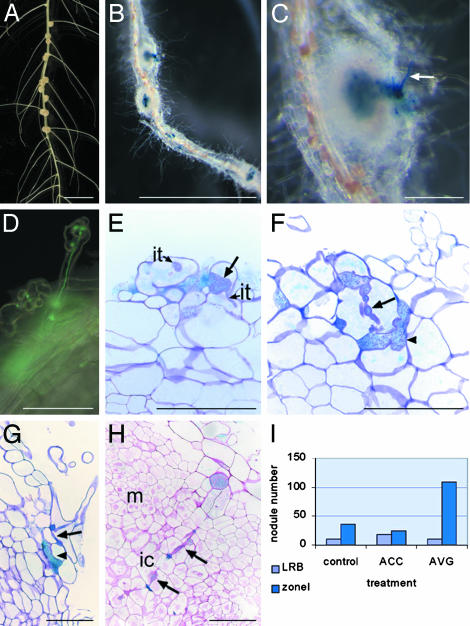
Fig. 1.
Features of S. rostrata nodulation. (A) Nodulated hydroponic S. rostrata root, 7 days postinoculation (DPI). Nodules are present at the lateral root bases. (B) GUS staining of a vermiculite-grown root nodulated by ORS571(pRG960SD-32). Nodules are distributed over the root (zone I nodules) 4 DPI. (C) Enlargement of B. Arrow indicates GUS-stained root hair. (D) Root hair with an infection thread containing A. caulinodans carrying a GFP marker. (E–G) Toluidine blue-stained sections through vermiculite-grown roots, 2 DPI with ORS571(pRG960SD-32), and stained for GUS. Arrows indicate initiating broad infection thread (E), an intracellular cortical infection thread (F), and an intercellular infection thread (G); arrowheads mark small infection pocket-like structures (F and G). (H) Ruthenium red-stained section through a developing zone I nodule, 4 DPI with ORS571(pRG960SD-32), and stained for GUS. Arrows indicate intracellular invasion track. (I)Influence of ethylene on lateral root base and on zone I nodulation on vermiculite-grown roots. The histogram presents the number of nodules derived from zone I or from lateral root base infection, 7 DPI, on roots grown in vermiculite (control), on vermiculite-grown roots to which ACC has been added 2 days before inoculation (ACC), and to which AVG has been added 2 days before inoculation (AVG). ic, infection center; it, infection thread; LRB, lateral root base nodule; m, meristem; zoneI, zone I nodules. (Bars = 1 cm in A and B,1mmin C, and 100 μmin D–H.)