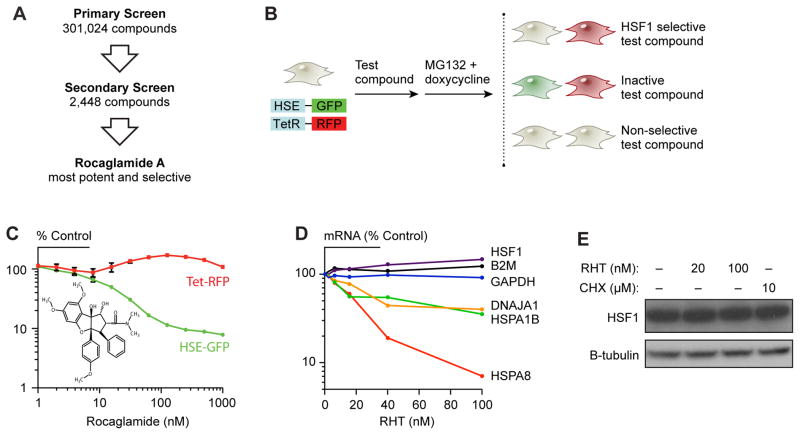
Fig. 3. Chemical screens reveal that targeting translation control inactivates HSF1.
(A) Flowchart outlining the steps in the high-throughput MLPCN screen for inhibitors of HSF1 activation. (B) Schematic of dual reporter cell line used to counter-screen primary screen hits. GFP expression is regulated by a heat shock inducible promoter. RFP expression is regulated by a doxycycline response element (TetR). (C) Effect of rocaglamide A on the HSE-driven GFP and doxycycline-driven RFP signals following incubation with 2.5 mM MG132 and 2 μg/ml doxycycline. Chemical structure of rocaglamide A is displayed in the inset. (D) Effect of RHT on HSF1-regulated and control endogenous mRNA transcript levels in M0-91 leukemia cells measured by nanostring nCounter following 6 hr. incubation with indicated concentrations of RHT. Levels of endogenous transcript are shown as percent of DMSO treated control. (E) HSF1 protein levels are not affected in M0-91 leukemia cells treated with RHT. Immunoblot shows the levels of HSF1 protein and the loading control (Tubulin) after a 6 hr. exposure to the indicated concentrations of RHT.