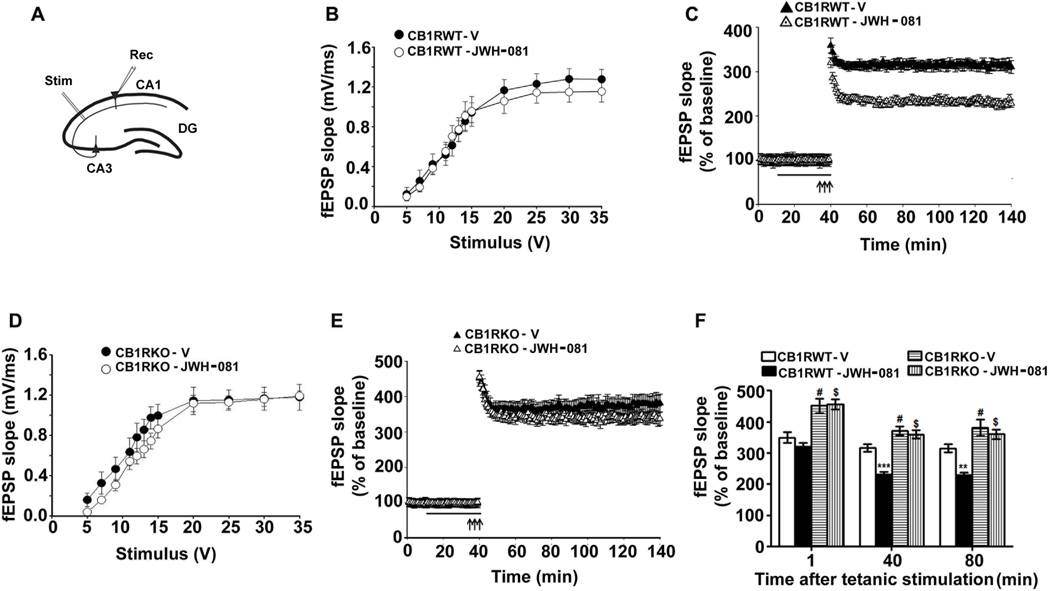
Figure 3.
JWH-081 inhibits LTP in hippocampal slices from adult CB1 receptor WT but not KO mice. (A) A schematic diagram showing the stimulating and recording electrode positions in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. (B) A summary graph showing the field input/output relationships in slices after treating WT slices with vehicle or JWH-081. (C) A time course of the averages of the fEPSP slopes in slices after treating WT slices with vehicle or JWH-081. (D) A summary graph showing the field input/output relationships in slices after treating KO slices with vehicle or JWH-081. (E) A time course of the averages of the fEPSP slopes in slices after treating KO slices with vehicle or JWH-081.The fEPSP slopes were normalized to the average value 10 min before stimulation in each experiment. Arrows denote the time of tetanic stimulation (4 pulses at 100 Hz, with bursts repeated at 5 Hz, each tetanus included three 10-burst trains separated by 15 s). For JWH-081 treatment experiments, after 10 min of baseline recording, hippocampal slices were perfused with JWH-081 (1.0 µM in DMSO) or vehicle (0.001% DMSO) for 30 min before inducing LTP with tetanic stimulation of the Schaeffer collateral pathway. (F) A combined plot of the averages of the fEPSP slopes for WT and KO slices with and without JWH-081 at several time points. Each point is presented as the mean ± SEM (n= 5 mice/group; 10 slices/group). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc tests; ***p < 0.001.