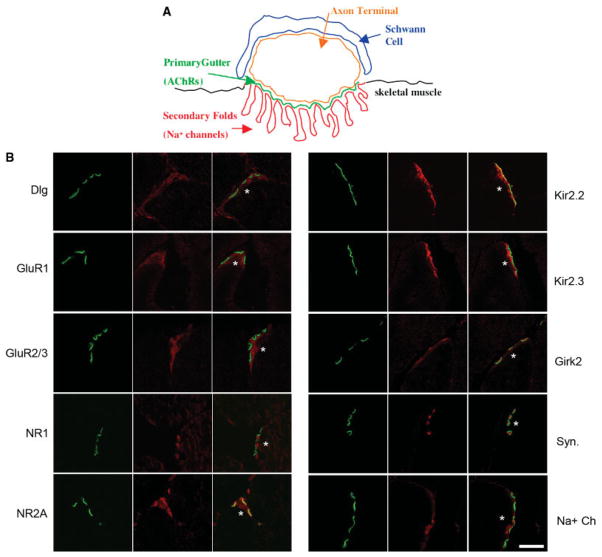
FIGURE 1.
Localization of glutamate receptors and potassium channels at NMJs. A: Schematic of the mammalian NMJ shows a Schwann cell (blue), the axon terminal (orange), and the skeletal muscle postsynaptic membrane composed of the primary gutter where AChRs localize (green) and the secondary folds (red) where Na+ channels localize to the bottom of the folds. B: Confocal analysis of immunolocalization at the NMJ, corresponding to the schematic in A, of Dlg and candidate interactors in 5-week-old normal mice. Transverse sections of quadriceps muscles were costained with each antibody (red) and Alexafluor 488 anti-bungarotoxin (green) to show localization of the AChRs located in the primary gutter of the postsynaptic membrane. Merged images are shown in the right panel. An asterisk (*) denotes the postsynaptic side of the NMJ. Antibodies specific for GluR1, GluR2/3, NR1, NR2A, Kir2.2, and Kir2.3 all show specific localization to the postsynaptic side of the NMJ in the skeletal muscle fiber. Girk2 specifically localizes to the presynaptic motor neuron axon terminal. The presynaptic marker synaptophysin (Syn.) and Na+ channels, known to localize to secondary folds of the postsynaptic membrane, are shown as controls. Scale bar = 3.7 μm.