Table 1. Relative energies of the eight diastereomeric transition states for the benzoin condensation of benzaldehyde with catalyst I.
 Transition-state geometry* |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | Enolamine | Enolamine face | Aldehyde face | Product configuration | ΔGrel, kcal/mol† |
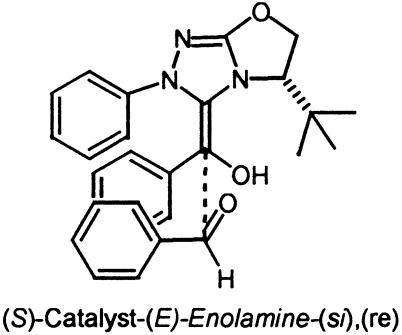
| S | E | si | re [TS1]‡ | S | 0 (0) |
| S | E | si | si [TS2]‡ | R | 2.8 (15.0) |
| S | Z | re | re | S | 2.9 (23.4) |
| S | E | re | re | S | 7.3 (21.6) |
| S | Z | si | re | S | 7.8 (4.5) |
| S | E | re | si | R | 8.4 (12.0) |
| S | Z | re | si | R | 9.8 (30.0) |
| S | Z | si | si | R | 17.8 (23.4) |
See Data Set 1, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site, for figures of structures and Cartesian coordinates.
Relative energies obtained by single-point B3LYP/6-31G(d) calculations. Energies in parentheses are relative energies calculated by using IMOMO (B3LYP/6-31G(d)//AM1).
Depicted in Fig. 5.
