Figure 3.
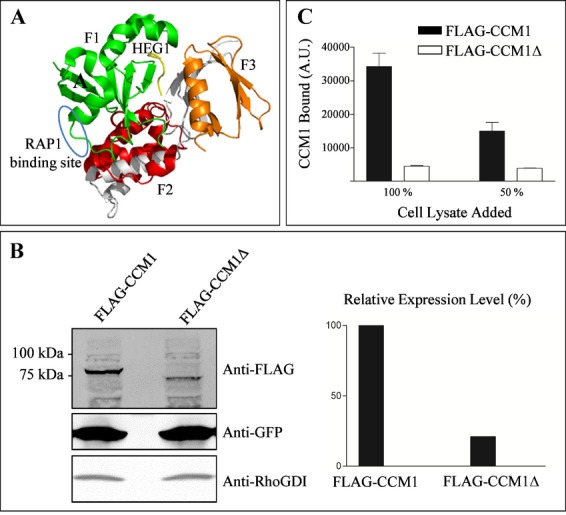
Single exon in-frame deletion within the FERM domain of CCM1 results in decreased protein expression and abrogates binding to HEG1. (A) Molecular view of CCM1 FERM domain bound to the HEG1 tail. The HEG1 tail is shown in yellow. The CCM1 FERM domain consists of three subdomains: F1 (green), F2 (red), and F3 (orange). The deletion in CCM1 encompassing the amino acids encoded by exon 18 is shown in gray and results in the deletion of structural elements within the FERM subdomains F2 and F3. The model also illustrates that the deletion spares the RAP1-binding site within CCM1 which is encircled in blue. (B) Western blot analysis of protein lysates. Compared with wild-type 84 kDa FLAG-CCM1 (lane 1), FLAG-CCM1:p.N607_K675del (FLAG-CCM1Δ) migrated at about 77 kDa (lane 2) and its expression was significantly reduced to ∼20% of the FLAG-CCM1 wildtype, while cotransfected GFP and endogenous RhoDGI levels were not altered. (C) Capture ELISA assays demonstrate that HEG1-bound significantly reduced amounts of FLAG-CCM1Δ (open bars) when compared to FLAG-CCM1 (black bars). Cell lysates were adjusted to match the FLAG-CCM1 expression levels.
