Figure 2. Propranolol inhibits NB viability and proliferation and is synergistic with SN-38.
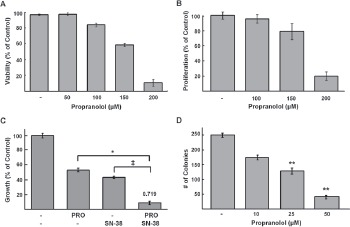
A, SK-N-AS cells were incubated with indicated doses of propranolol for 24h and cell viability was determined using trypan blue exclusion method. Results are expressed as a mean percentage of trypan blue negative cells (live cells); data shown are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as means of triplicates ± s.d. B, SK-N-SH cells were treated with indicated doses of propranolol for 24h. Cell proliferation was assessed by BrdU incorporation. Results are a mean percentage of control cells. C, alamarBlue assays were performed on SK-N-AS cells treated with increasing doses of propranolol and SN-38 at a ratio of 10,000:1 (100μM propranolol: 0.01μM SN-38) for 48hr. Results are expressed as percentage compared to controls. The combination index (CI) was determined based on the Chou-Talalay method is shown on the top of the bar representing combination treatment * p= 0.008, ‡ p= 0.0009. D, Concentration-dependent effects of propranolol on clonogenic growth. SK-N-AS cells were treated for 14 days with propranolol at indicated doses or media alone (control); colonies were detected by staining with crystal violet. Bars represent the mean number of colonies of triplicate wells from three independent experiments ± s.d; ** p <0.001 students t-test.
