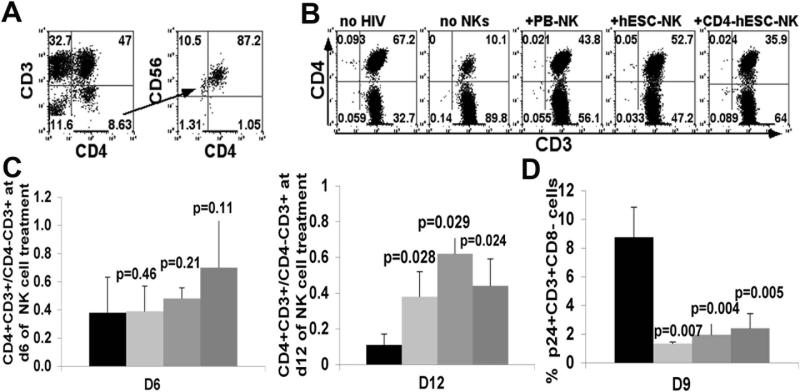
Figure 4. hESC-NK cells and CD4ζ-hESC-NK cells suppress HIV replication in peripheral blood.
Two weeks after PBL reconstitution, mice were infected with HIV NL4-3 and treated with NK cells next day. Peripheral blood was then collected at day6, 9 and 12 with or without NK cell treatment. HIV infection was evaluated by CD4+ T cell depletion and HIV+ cell percentage in peripheral blood. CD4+ T cell level was determined by flow cytometry for CD4+CD3+/CD4−CD3+ ratios. HIV infected human cells were evaluated by intracellular staining for gag p24+. (A) CD45+CD3−CD4+ cells that were CD56+ and GFP+ detected in peripheral blood of mice treated with CD4-hESC-NK cells after day 6. (B) Human CD45+ cells that express CD3 and CD4 were assessed in peripheral blood of HIV-1-infected NSG mice treated with or without NK cells at day 6. All cells were hCD45+ gated. Flow cytometry plots are representative of 1 mouse of each condition in at least 3 independent experiments with a minimum of 3 mice in each experimental group. (C) CD4+ T cell levels in peripheral blood of HIV infected mice determined by CD4+CD3+/CD4−CD3+ ratios at day 6 (left panel) and day 12 (right panel) of NK cell treatment. All mice were analyzed prior to HIV infection to set up baseline CD4+CD3+/CD4−CD3+ratios. (D) Suppression of HIV infection was evaluated by the percentages of p24+ cells in all hCD3+CD8− from peripheral blood at day 9 of NK cell treatment. Data in (C) and (D) represent the average of one of three separated experiments with at least 3 mice in each group, the error bars indicate the mean +/− the SD. Statistical comparison of CD4+ T cell level and % p24+CD3+CD8− in NK treated mice to untreated mice was performed using Student's t test. P values are provided for each indicated comparison.