Table 3. Measures evaluated for introgression populations resulting from different crossing and selection schemes.
| Scheme |
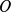
|
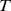
|
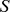
|
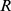
|
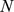
|
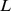
|
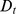
|
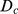
|
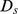
|
HT |
| Basic crossing schemes | ||||||||||
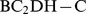
|
99.9 | 8.3 | 691 | 2.9 | 6.2 | 28.7 | 8.3 | 38.9 | 98.7 | 720 |
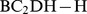
|
100.0 | 8.9 | 751 | 2.7 | 6.4 | 29.2 | 8.9 | 37.3 | 94.1 | 720 |
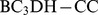
|
99.2 | 5.1 | 457 | 4.4 | 3.8 | 29.8 | 5.0 | 35.2 | 97.8 | 1080 |
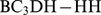
|
99.8 | 5.2 | 487 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 29.8 | 5.1 | 33.3 | 94.2 | 1080 |
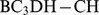
|
99.6 | 5.2 | 469 | 4.3 | 3.8 | 30.5 | 5.1 | 35.1 | 93.7 | 1080 |
| Crossing schemes with high selection intensity | ||||||||||
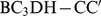
|
99.3 | 3.6 | 389 | 5.1 | 3.0 | 27.8 | 3.6 | 27.7 | 98.8 | 2160 |
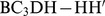
|
99.9 | 3.8 | 406 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 29.7 | 3.8 | 29.1 | 99.4 | 2160 |
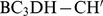
|
99.6 | 3.9 | 399 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 30.0 | 3.8 | 29.9 | 99.0 | 2160 |
| Crossing schemes with selection in the final BC generation | ||||||||||
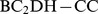
|
99.9 | 7.8 | 676 | 3.0 | 5.9 | 28.7 | 7.8 | 41.0 | 98.9 | 1440 |
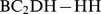
|
100.0 | 8.1 | 716 | 2.8 | 6.0 | 29.0 | 8.1 | 38.9 | 99.3 | 1440 |
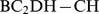
|
99.9 | 8.5 | 679 | 2.9 | 6.0 | 30.4 | 8.5 | 43.7 | 98.8 | 1440 |
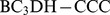
|
99.1 | 4.9 | 457 | 4.4 | 3.7 | 30.2 | 4.8 | 35.8 | 98.0 | 1800 |
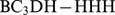
|
99.9 | 4.8 | 464 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 31.0 | 4.7 | 33.9 | 98.9 | 1800 |
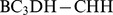
|
99.6 | 4.8 | 450 | 4.4 | 3.5 | 31.4 | 4.7 | 35.0 | 98.5 | 1800 |
| Crossing schemes with increasing population sizes | ||||||||||
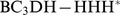
|
99.9 | 5.0 | 492 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 29.7 | 5.0 | 33.3 | 98.4 | 1440 |
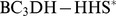
|
99.8 | 4.9 | 484 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 29.4 | 4.8 | 32.5 | 97.5 | 1440 |
| Basic crossing schemes | ||||||||||
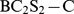
|
100.0 | 11.4 | 1021 | 2.0 | 7.3 | 26.4 | 9.3 | 41.4 | 97.6 | 720 |
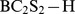
|
100.0 | 11.4 | 1073 | 1.9 | 7.4 | 25.9 | 9.3 | 36.3 | 90.4 | 720 |
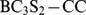
|
99.3 | 6.9 | 684 | 2.9 | 4.5 | 27.7 | 5.7 | 39.2 | 97.0 | 1080 |
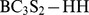
|
99.9 | 6.3 | 702 | 2.8 | 4.4 | 26.3 | 5.3 | 33.0 | 90.3 | 1080 |
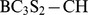
|
99.7 | 6.4 | 681 | 2.9 | 4.3 | 26.9 | 5.3 | 35.0 | 89.9 | 1080 |
| Crossing schemes with high selection intensity | ||||||||||
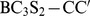
|
99.5 | 5.1 | 585 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 26.6 | 4.3 | 32.3 | 98.8 | 2160 |
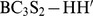
|
99.9 | 5.1 | 591 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 27.8 | 4.4 | 32.1 | 98.9 | 2160 |
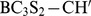
|
99.7 | 5.2 | 581 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 28.2 | 4.4 | 33.4 | 98.4 | 2160 |
| Crossing schemes with selection in the final BC generation | ||||||||||
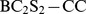
|
99.3 | 10.5 | 795 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 27.2 | 8.3 | 48.3 | 98.0 | 1080 |
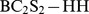
|
99.9 | 9.7 | 785 | 2.5 | 6.2 | 27.0 | 7.9 | 42.8 | 98.8 | 1080 |
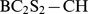
|
99.8 | 9.7 | 761 | 2.6 | 6.1 | 27.6 | 7.9 | 45.9 | 98.4 | 1080 |
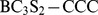
|
98.3 | 7.1 | 588 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 30.5 | 5.7 | 44.6 | 97.5 | 1440 |
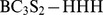
|
99.7 | 5.9 | 510 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 31.0 | 5.0 | 38.1 | 98.6 | 1440 |
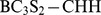
|
99.3 | 6.0 | 509 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 31.3 | 5.0 | 39.5 | 98.2 | 1440 |
| Crossing schemes with increasing population sizes | ||||||||||
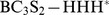
|
99.7 | 5.8 | 508 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 30.7 | 4.9 | 38.0 | 98.7 | 1440 |
|
99.8 | 5.1 | 596 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 26.1 | 4.3 | 30.4 | 96.2 | 1400 |
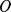 : donor genome coverage in percent;
: donor genome coverage in percent; 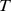 : depth of donor genome coverage;
: depth of donor genome coverage; 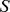 : number of disjunct genome segments;
: number of disjunct genome segments; 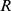 : resolution;
: resolution; 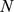 : number of donor segments per IL;
: number of donor segments per IL; 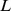 : length of donor segments per IL in cM;
: length of donor segments per IL in cM; 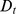 : total donor genome proportion in percent;
: total donor genome proportion in percent; 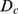 : donor genome proportion of carrier chromosomes in percent;
: donor genome proportion of carrier chromosomes in percent; 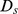 : donor genome proportion of target segments in percent; HT: the required number of HT assays. Measures are arithmetic means over 1,000 replications.
: donor genome proportion of target segments in percent; HT: the required number of HT assays. Measures are arithmetic means over 1,000 replications.
