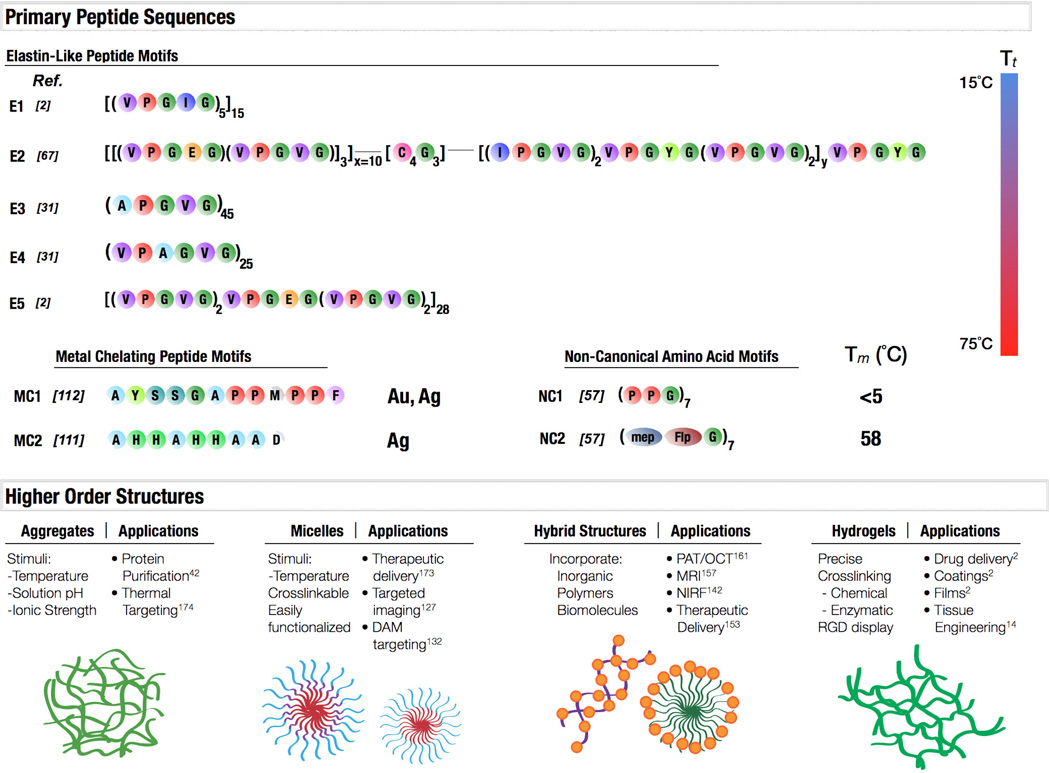
Fig. 8.
A schematic depicting primary peptide sequences, associated properties, and potential applications. Elastin-like polypeptides E1-E5 exhibit transition temperatures between 15°C and 75°C. E1 and E5 are elastomeric-like. E2 is an amphiphilic diblock copolymer with an intermediate crosslinking domain. E3 and E4 represent potential for hexapeptide elastin-like motifs, shown to have a wide range of temperature and structural variability. Polypeptides have also been identified which chelate metallic ions, such as MC1, which is capable of capturing both gold and silver. MC2 has been shown to efficiently bind silver. Further expansion of the basic collagen motif, NC1, with modified prolines (2S,4R)-4-methylproline (mep) and (2S,4R)-4-fluoroproline (Flp) showed how side chain modification could stabilize the collagen triple helix, concepts that could be applied to many protein motifs. These protein motifs can then organize into higher order structures in response to environmental stimuli or composition, such as protein aggregates, micelles, hybrid organic-inorganic structures, and hydrogels. All of these protein materials can be utilized in a variety of applications.