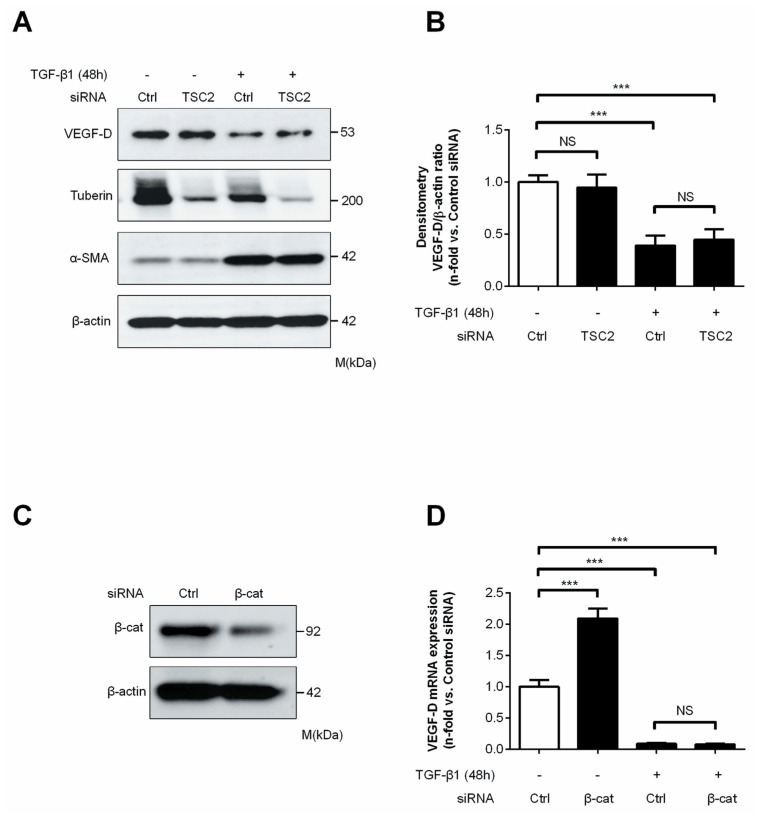
Figure 5.
Knockdown of TSC2 or β-catenin is not sufficient to block TGF-β1–induced suppression of VEGF-D in MRC-5 cells. (A, B) MRC-5 cells were transfected with control siRNA (Ctrl) or TSC2 siRNA for 24 h, serum starved for 24 h and then incubated in serum-free medium in the absence or presence of TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for 48 h. (A) Equal amounts of protein from whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against VEGF-D, tuberin, α-SMA and β-actin. (B) Ratio of VEGF-D to β-actin density was expressed as the fold-change relative to control siRNA alone. (C) β-Catenin (β-cat) knockdown efficiency in MRC-5 cells 48 h after transfection, as determined by Western blot analysis. (D) Real-time PCR analysis of total RNA extracted from MRC-5 cells transfected as in (C) for 24 h, serum-starved for 24 h and then stimulated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for 48 h. VEGF-D mRNA levels were normalized to β2-macroglobulin mRNA and expressed as the fold-change relative to control siRNA alone. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001, NS, not significant, by one-way ANOVA.