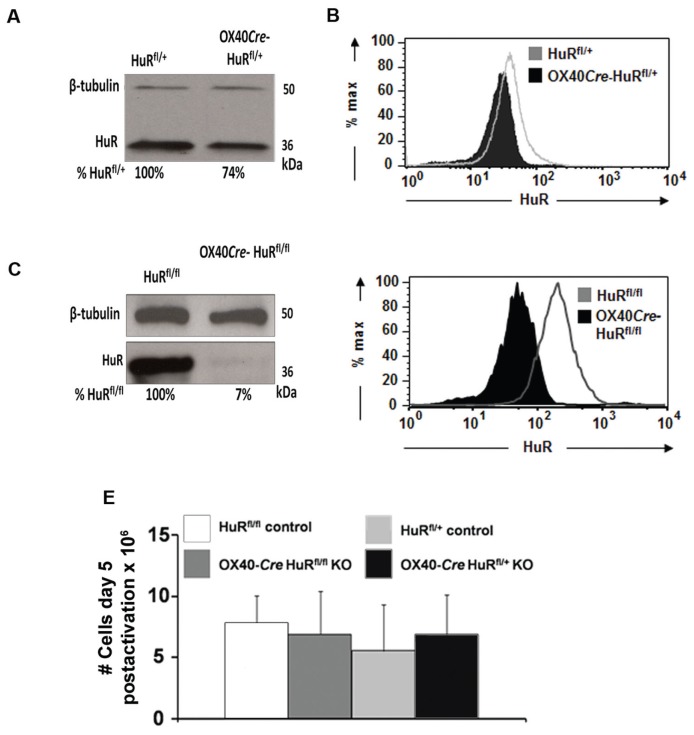
Figure 1.
OX40-Cre HuRfl/+ and OX40-Cre HuRfl/fl knockout mice display significant decreases in HuR protein levels. (A) Western blot analysis of HuR expression (and β-tubulin as loading control) in activated T cells from OX40-Cre HuRfl/+ compared with HuRfl/+ control mice and (C) in activated T cells from OX40-Cre HuRfl/fl compared with HuRfl/fl control mice. (B) Intracellular HuR staining assessed by fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis in activated T cells from OX40-Cre HuRfl/+ and HuRfl/+ control mice and (D) from OX40-Cre HuRfl/fl and HuRfl/fl control mice. (E) Proliferation assay reveals HuR knockout does not affect T-cell proliferation (mean ± standard error of the mean [SEM]; n = 3). Western blot and intracellular HuR staining representative of n = 3.