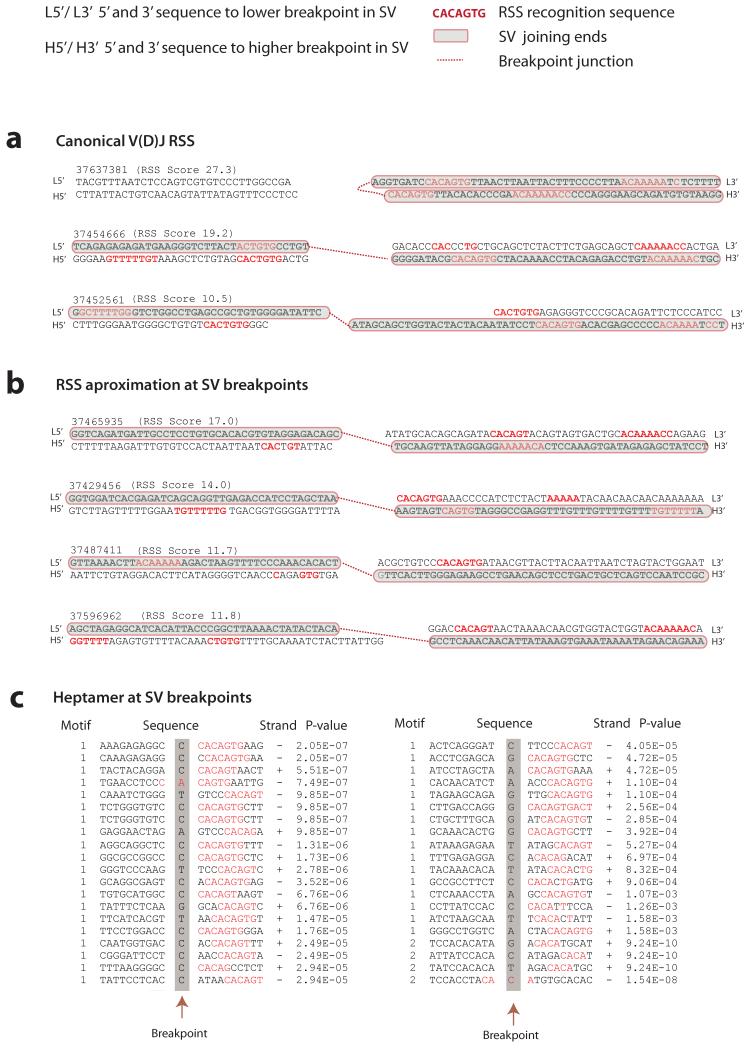
Figure 2. Evaluation of V(D)J recombination motifs.
RSS heptamer and nonamer sequences are shown in red, spacing annotates position of breakpoint. Retained sequence flanking the breakpoint junction is shown in bold black, shaded in grey with red borders. Genomic sequence is annotated 5′ to 3′ as presented in the reference genome (+) strand. For each rearrangement, the first line indicates the sequence flanking the lower breakpoint, the second line corresponds to the sequence flanking the higher breakpoint. The RSS Score for each rearrangement is shown in parenthesis. A dotted red line annotates the breakpoint junction. For more detailed annotation please refer to Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Rearrangements at the V(D)J locus showing examples of canonical V(D)J recombination signal sequences (in red) in close proximity to the breakpoint junctions. (B) Close approximation to RSS sequence motifs near the breakpoint junction of confirmed structural variants in ETV6-RUNX1 ALL. Represented in this figure are sequence motifs spanning the breakpoints for TBL1XR1 (RgID 37439593); FAF1 and CDKN2C (RgID 37429456); BTG1 (RgID 37487411) and RgID 37596962 showing chr1:190,815,392-190,815,481 joining to chr1:190,926,946-190,927,035. (C) Heptamer sequences identified by agnostic motif search analysis using MEME. A representation of 40 of the 164 breakpoints identified to harbor heptamer like motifs within 20bp of the breakpoint junction. In red, the bases contributing to the motif identification in the ETV6-RUNX1 ALL dataset. Heptamer p values are annotated as calculated by MEME.