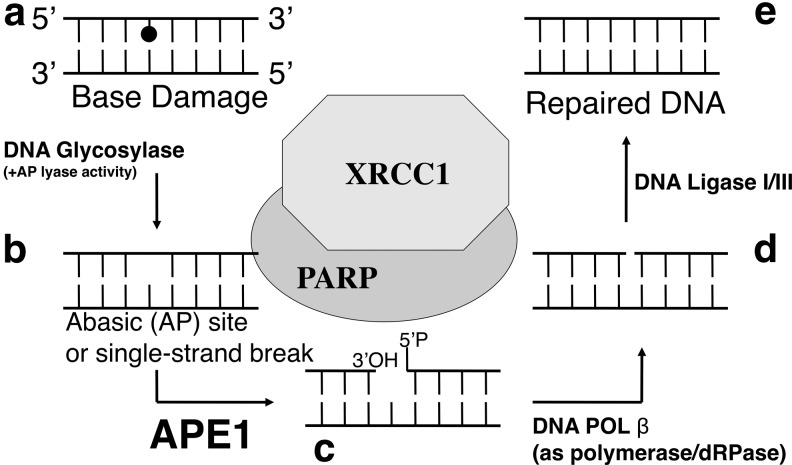
FIG. 4.
Basic steps of BER. (a) Abnormal base damage, including oxidative and alkylated bases (e.g., 8-oxoG, N3-methylG, and so on) are recognized and removed by DNA glycosylases. (b) Consequently, either AP sites or DNA SSBs are generated at the damaged sites. (c) APE1 generates 3′-OH termini for subsequent DNA repair synthesis step processed by DNA polymerases. (d) pol β is the primary BER DNA polymerase, which also removes 5′-ribose moieties to generate 5′-P termini at the gap. (e) The DNA nicks with 3′-OH and 5′-P ends (without gaps) will be ligated by DNA ligase I or III to complete the BER process. 8-oxoG, 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine; SSB, single-strand break; pol β, polymerase beta.