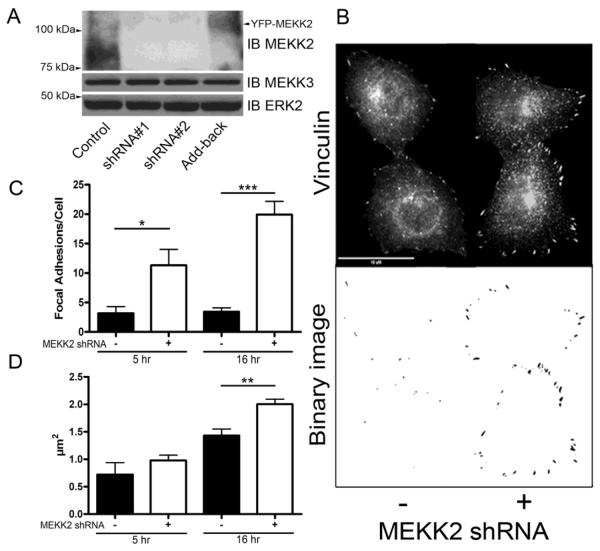
Fig. 3.
MEKK2 knockdown stabilizes focal adhesions. (A) Immunoblot of MDA-MB 231 lysates displaying expression of MEKK2 (upper panel), MEKK3 (middle panel), and total ERK2 as a loading control (lower panel) from control cells, cells treated with MEKK2 shRNA #'s 1 and 2, or MEKK2 shRNA with stably expressed shRNA-resistant MEKK2 (Add-back). (B) Fluorescence microscopy with anti-vinculin antibodies was used to detect focal adhesions in MDA-MB 231 cells attached to fibronectin. Representative images after 16 hours of attachment showing vinculin-associated focal adhesions in control cells (upper panel, left) or cells with MEKK2 shRNA (upper panel, right). Original images were converted to binary images (lower panel) for analysis. (C) Quantification of number of focal adhesions per cell, and (D) mean area of individual focal adhesions after attachment to fibronectin for 5 hours and 16 hours in MDAMB 231 cells. The data represented in the graphs was derived from at least three independent experiments. Total cells analyzed is n = 48 control MDA-MB 231 cells, and n= 46 MDA-MB 231 cells with stable MEKK2 knockdown (D). The data represented in the graphs was derived from at least three independent experiments. *p <0.05, **p <0.01, ***p <0.001. Scale bar represents 10 μm.