Fig. 7.
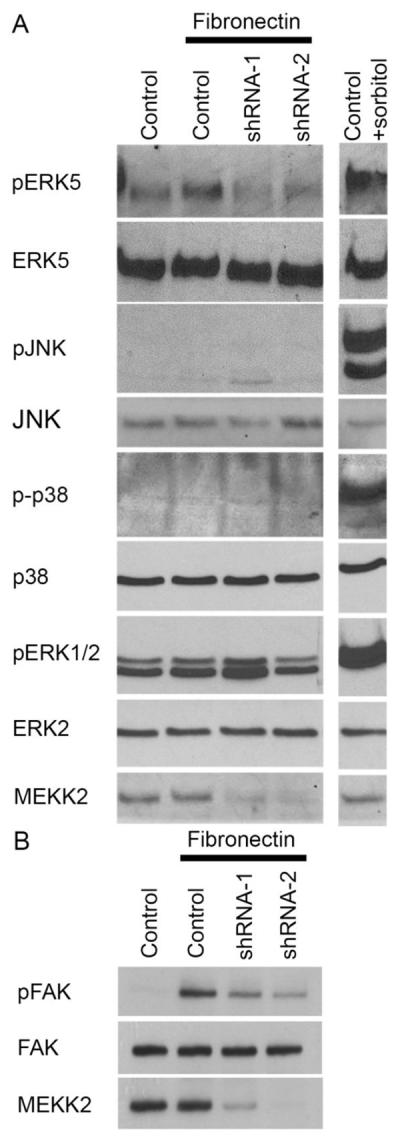
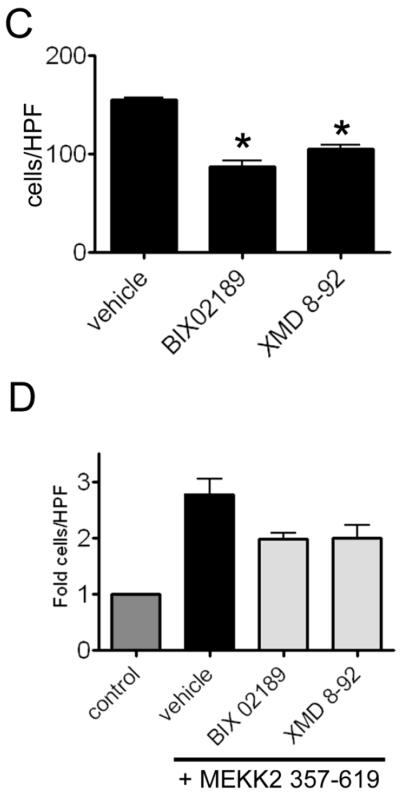
MEKK2 regulates FN-induced signaling. (A and B) MDA-MB 231 control cells and cells with stable MEKK2 knockdown were seeded on uncoated culture plates (not treated) or plates coated with fibronectin. Positive control cells for JNK, ERK5, p38 or ERK1/2 activation were exposed to 0.2M sorbitol for 15 minutes. (B) Immunoblots showing the level of fibronectin-induced FAK Y397 phosphorylation (upper panel) in MDA-MB 231 control cells and in cells with stable MEKK2 knockdown. Total FAK immunoblot (middle panel) shows equal protein content of test lanes and MEKK2 immunoblot (bottom panel) confirms MEKK2 knockdown. (C and D) Graphical representation of a transwell migration assays of MDA-MB 231 cells treated with vehicle (DMSO), BIX02189 MEK5 inhibitor (10 μM) or ERK5 inhibitor XMD 8–92 (5 μM) during the 5 hour migration period. (D) Serum-induced chemotaxis of MDA-MB 231 cells that stably express activated MEKK2 (357–619) is compared to that of MDA-MB 231 cells that express endogenous MEKK2 (control) or cells that express MEKK2 (357–619) but migrated in the presence of the inhibitors. Results are compiled from three independent experiments.