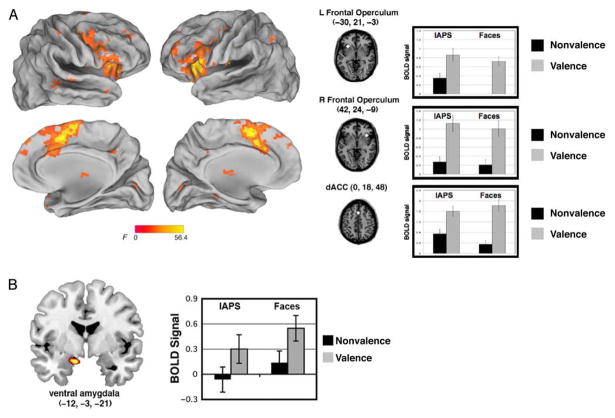
Figure 5.
Brain regions active for the main effect of task. (A) Three task control regions, comprising the cingulo-opercular network, showed greater activity during the valence task, as compared with the nonvalence task (gender judgment for face stimuli, social judgment for IAPS scenes). (B) A region of ventral amygdala showed greater activity to ambiguous stimuli during the valence task.