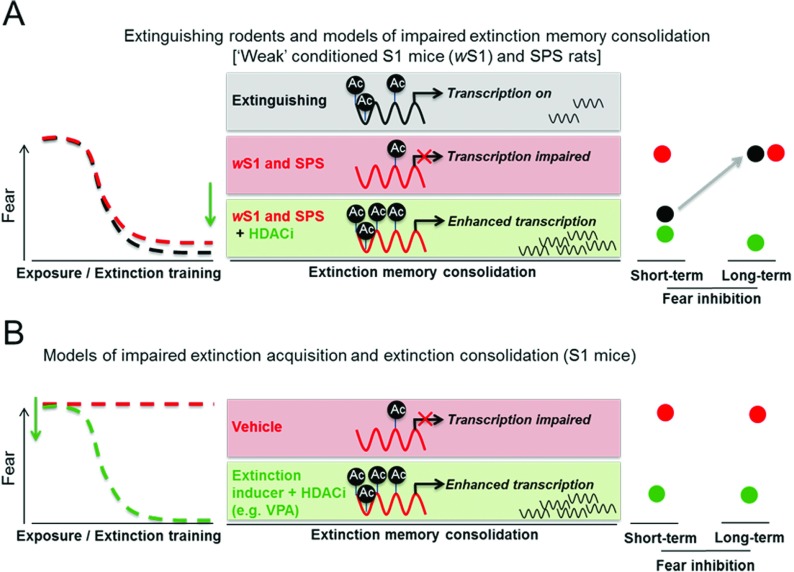
Figure 3. HDAC inhibitors augment fear extinction and rescue cognitive deficits in animal models of impaired extinction.
(A) Normal extinguishing rodents display fear reduction during a exposure-based fear extinction training session (termed ‘extinction acquisition’; black broken line) and extinction-induced increases in histone acetylation (black filled circle) during extinction memory consolidation. Evidence of successful fear extinction consolidation is observed with low fear levels during a retrieval test 24 h later (short-term extinction retrieval; black filled circle). However, long-term fear inhibition is lacking as return of fear can be observed. Weak conditioned S1 (wS1) mice and SPS rats display intact extinction acquisition (red broken line), but are unable to consolidate/retrieve this memory (red filled circle), probably due to insufficient increases in extinction-induced histone acetylation and subsequent gene expression changes. Post-extinction training administration of HDAC inhibitors (MS-275, SAHA; green arrow) in wS1 and SPS rats can induce histone acetylation with subsequent rescue of extinction-consolidation deficits and promotion of long-term fear inhibition (green filled circles). (B) Normal conditioned S1 display in addition also impaired extinction acquisition (red broken line). Pharmaceutical adjuncts such as VPA (green arrow) that induce extinction acquisition (positive training effect, i.e. fear reduction), as well as HDAC inhibition, are required to rescue the pronounced extinction deficits and promote long-term fear inhibition (green filled circles) in these mice. Abbreviations: Ac, acetylated histone; HDACi, HDAC inhibitors.