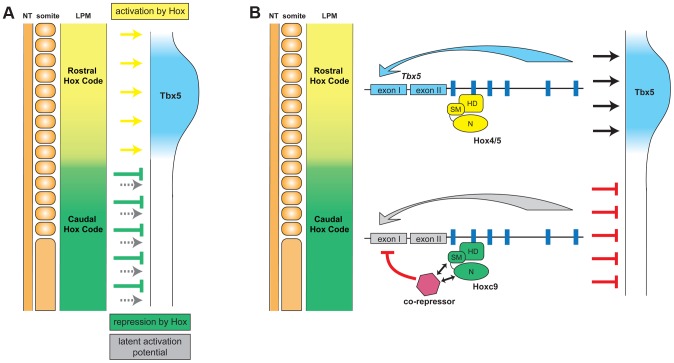
Figure 7. Model for the combinatorial regulation of forelimb-restricted Tbx5 expression by distinct paralogous Hox gene inputs.
A. Hox genes expressed in the rostral forelimb-forming LPM induce Tbx5 expression (yellow arrows). In the caudal flank there is a latent capacity to activate Tbx5 expression (grey arrows) that is normally masked by the presence of caudally-expressed Hox genes (Hoxc8, Hoxc9 and Hoxc10) that repress expression of Tbx5 (green arrows). Thus, a combination of Hox colinear expression and the specific activator or repressor activities of distinct Hox protein paralogs dictates positioning of forelimb-forming region. B. The transcriptional repression of Tbx5 is controlled by caudally-expressed Hox genes, such as Hoxc9, bound on Hbs2. This site is occupied both in forelimb-forming region (Hox PG4/5) and in caudal LPM (Hoxc9). However, only Hoxc9 forms a repressive complex by recruiting co-repressor(s). HD, homeodomain; SM, specificity module; N, N-terminus.