Figure 2. Predicted and observed actionable genotypes and associated medication exposures.
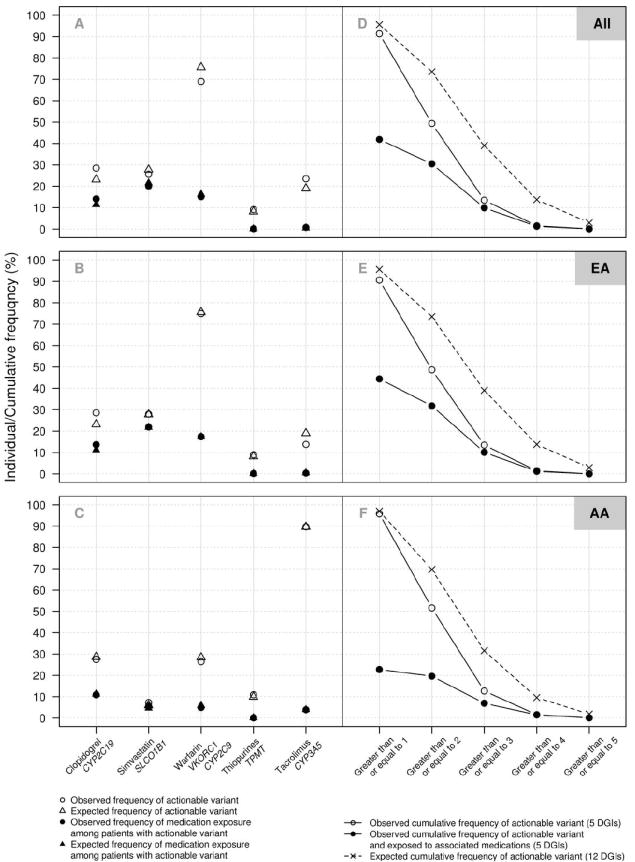
In panels A-C, for each Drug-Genome Interaction (DGI), the frequencies of expected actionable genotypes based on reported minor allele frequencies (open triangles), observed actionable genotypes (open circles), expected frequency of medication exposures among patients with actionable genotypes (filled triangles) and observed actionable genotype with exposure to the associated medication (filled circles) are shown for all 9,589 genotyped patients (A), 6,986 patients of European-American descent (B), and 953 patients of African-American decent (C). Clopidogrel exposure includes clopidogrel and/or prasugrel, the alternative agent. Statin exposure includes simvastatin and/or alternative HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin). In panels D-F, cumulative frequency of individuals having observed actionable genotypes based on the five currently implemented DGIs (open circles), cumulative frequency of individuals with actionable genotypes exposed to associated medications (filled circles), and predicted cumulative frequency of actionable genotypes based on a total of 12 pharmacogenes (x’s) are shown for all genotyped patients (D), patients of European-American descent (E), and patients of African-American decent (F).
