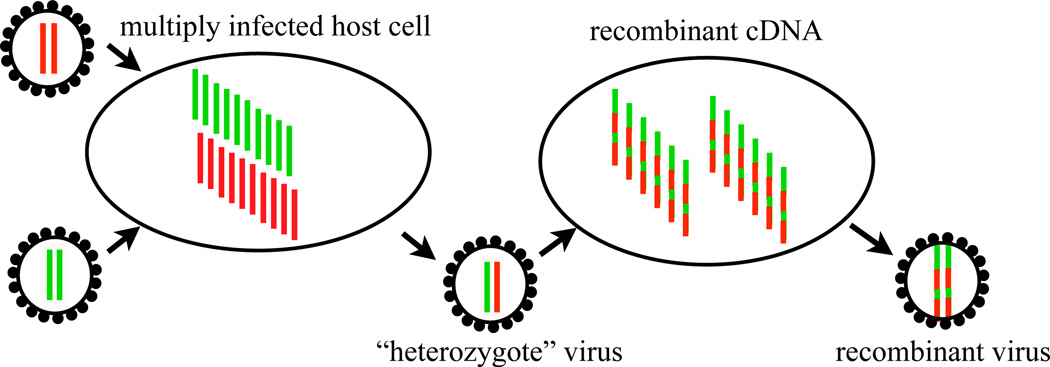
Figure 5.
Each HIV particle contains two copies of its RNA genome, from which one complementary DNA strand is produced and integrated into the host cell genome. The two RNA strands are combined by template switching of the reverse transcriptase enzyme, which can happen up to 10 times per replication [31]. The in vivo recombination rate, however, is limited by the probability that a host cell is infected by genetically distinct viruses, illustrated on the left. The effective recombination rate combining these two processes is estimated to be on the order of 10−5 per nucleotide per generation [37, 6, 27], which implies a coinfection rate on the order of a few percent.