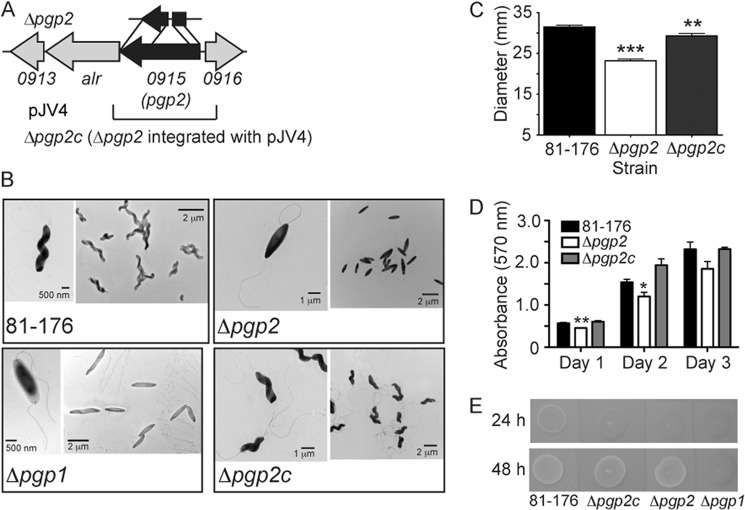
FIGURE 1.
C. jejuni 81-176 pgp2 gene locus, pgp2 mutant straight morphology, and defects in motility, biofilms, and CFW reactivity. A, the pgp2 mutant was constructed by deleting a 439-bp internal fragment of pgp2; the approximate location of this deletion is shown above the gene cluster and is denoted by the Δpgp2 strain designation. The region cloned into the integrative vector pRRC (pJV4; CmR) used for complementation is shown below the gene cluster. B, negatively stained TEM images of the helical C. jejuni 81-176 strain, the straight Δpgp1 (described previously (11)) and Δpgp2 mutant strains with intact flagella, and complemented strain Δpgp2c with restored helical morphology. C, Δpgp2 exhibited a 26.3% decrease in motility, as assayed by measuring halo diameters in soft agar plates. S.E. (error bars) was calculated from 10 measurements. D, Δpgp2 was defective for biofilm formation, which was complemented in Δpgp2c. Biofilm formation was assessed by crystal violet staining of standing cultures in borosilicate tubes and quantification of dissolved crystal violet at 570 nm. S.E. values were calculated from triplicate cultures and are representative of three independent experiments. E, Δpgp2 was hypofluorescent relative to wild-type 81-176 after 24 h but not 48 h of growth on plates containing 0.002% CFW (in contrast, Δpgp1 remained hypofluorescent after 48 h of growth (11)). Δpgp2 hypofluorescence was not restored by complementation. *, statistically significant difference using the unpaired Student's t test, with *, **, and *** indicating p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.0001, respectively.