FIGURE 5.
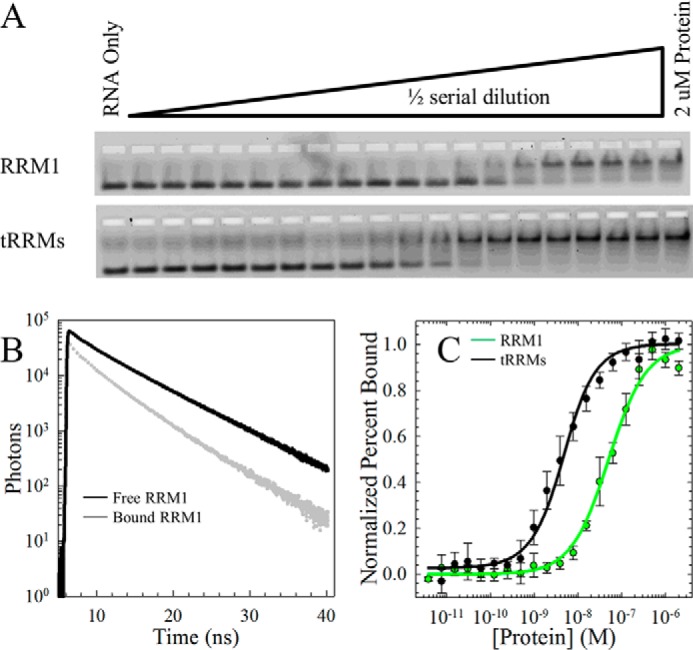
Tethering the RRM domains enhances the RNA binding affinity compared with RRM1. A, EMSA of increasing concentrations of RRM1 (top) and tRRMs (bottom) to a fixed concentration of 5′-carboxyfluorescein (FAM)-labeled (UG)6. The upper and lower bands on the native polyacrylamide gel represent the bound and free fractions of labeled RNA, respectively. B, Trp lifetimes of RRM1 alone (black) or bound by (UG)6 (gray) reveal a decrease in lifetime in the Trp on RRM1 upon binding. Trp lifetimes are insensitive to RRM2 due to a lack of Trp in this domain. Trp lifetimes were performed as a function of nucleic acid to a fixed concentration of RRM1 and tRRMs. C, quantification of the EMSA. Each data set is an average of three independent runs and modeled to the quadratic binding equation (Equation 6). A complete summary of binding affinities for tRRMs, RRM1, RRM2, and RRM2c is provided in Table 2.
