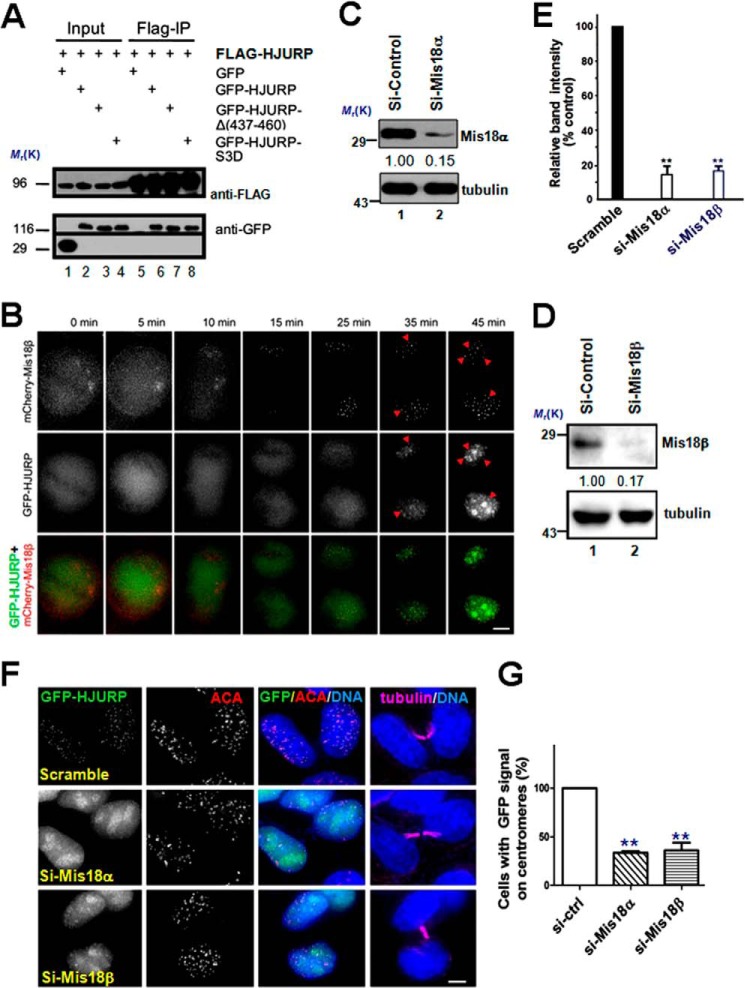
FIGURE 4.
HJURP is recruited to centromeres through binding to Mis18β. A, extracts of 293T cells co-expressing FLAG-HJURP and different GFP-HJURP constructs as indicated were subjected to anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation and then followed by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG and anti-GFP antibody, respectively. B, representative image stills of live cell imaging of HeLa cell co-expressing GFP-HJURP and mCherry-Mis18β. The arrowheads pinpoint the co-localization sites. Scale bar, 5 μm. C, immunoblots of lysates from cells transfected with siRNA against Mis18α or a scramble sequence siRNA (a negative control; lane 1) probed with the indicated antibodies. 48 h after siRNA transfection, cells were collected and assayed by Western blotting of Mis18α and tubulin, respectively. D, immunoblots of lysates from cells transfected with siRNA against Mis18β or a scramble sequence siRNA (a negative control; lane 1) probed with the indicated antibodies. 48 h after siRNA transfection, cells were collected and assayed by Western blotting of Mis18β and tubulin, respectively. E, quantification of Mis18α and Mis18β protein suppression by siRNA. Values represent the means ± S.E. (error bars) from three independent experiments (**, p < 0.01 compared with that of scramble-transfected cells). F, Representative images of HeLa cells stably expressing GFP-HJURP cells treated with different siRNAs, as indicated. 48 h after transfection, cells were fixed and co-stained for ACA (red), microtubule (magenta), and DNA (blue). Cells with midbody were selected to show they were in early G1 phase. Scale bar, 5 μm. G, bar graph showing the quantification of percentage of cells with GFP-HJURP-positive centromeres for siRNA treatments described in F. The data represent mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. More than 53 early G1 phase cells (midbody-positive) were analyzed per condition. **, p < 0.01 compared with that of scramble transfected cells.