FIGURE 4.
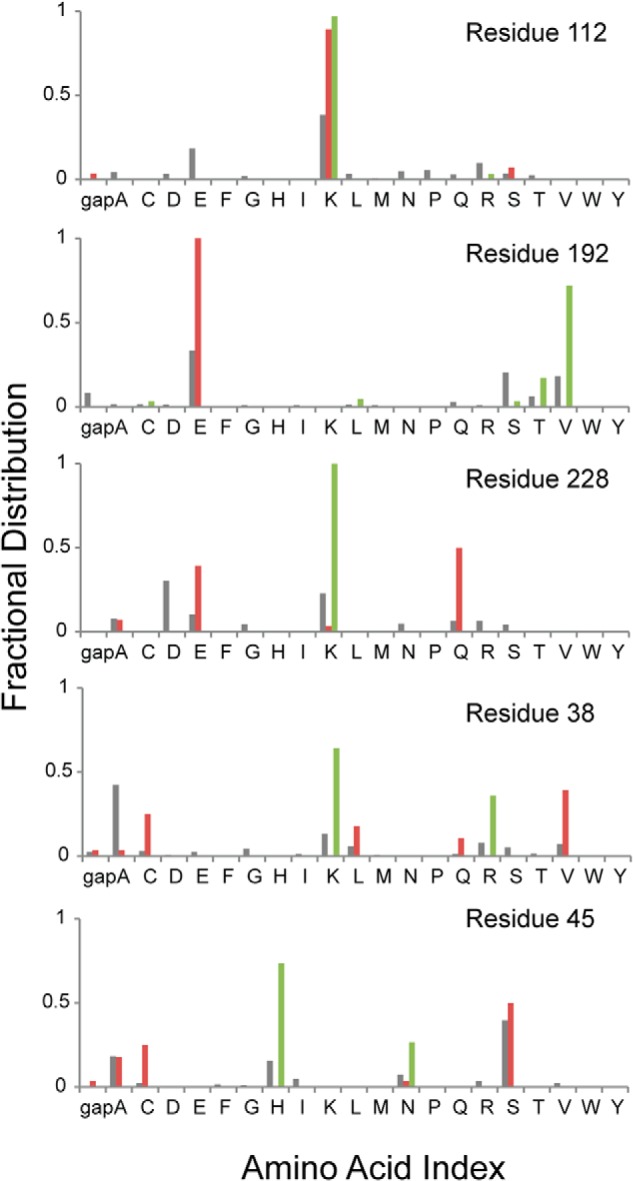
Conservation of signature residues associated with regulatory mechanisms of FBPase. Amino acid types associated with sequence positions essential for AMP inhibition (residue 112), tetramer formation (residue 192), Glc-6-P inhibition (residue 228), anion activation (residue 38), and central cavity formation (residue 45) are presented from top to bottom. Gray, red, and green columns represent the amino acid type for all FBPases, eukaryotic FBPases, and E. coli-like FBPases, respectively.
