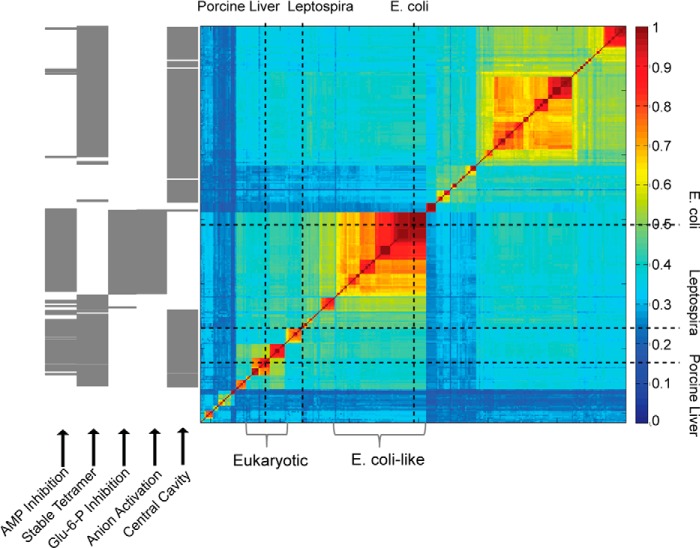
FIGURE 5.
Similarity matrix of Type I FBPase sequences and the prediction of structural and regulatory properties. The fraction of identical residues in sequence pairs are represented by color according to the scale to the right of the similarity matrix. The positions of eFBPase, pFBPase, and lFBPase are marked by vertical and horizontal dotted lines. FBPases from eukaryotic systems and E. coli-like FBPases are indicated by brackets. Regulatory properties are predicted (gray bar) according to residue types associated with key positions in the amino acid sequence. AMP inhibition requires serine or threonine for residue 31, lysine or arginine for residue 112, and tyrosine for residue 113. Tetramer stability requires lysine or arginine for residue 42 and glutamate for residue 192. Glc-6-P inhibition requires tyrosine for residue 216, lysine or arginine for residue 228, and glutamine for residue 231. Anion activation requires glycine for residue 14, lysine or arginine for residue 38, lysine or arginine for residue 88, and not glutamate for residue 192. The presence of a central cavity (AMP/Fru-2,6-P2 synergism) requires small side chains (glycine, alanine, cysteine, serine, or gap) for residue 45.