Fig. 1.
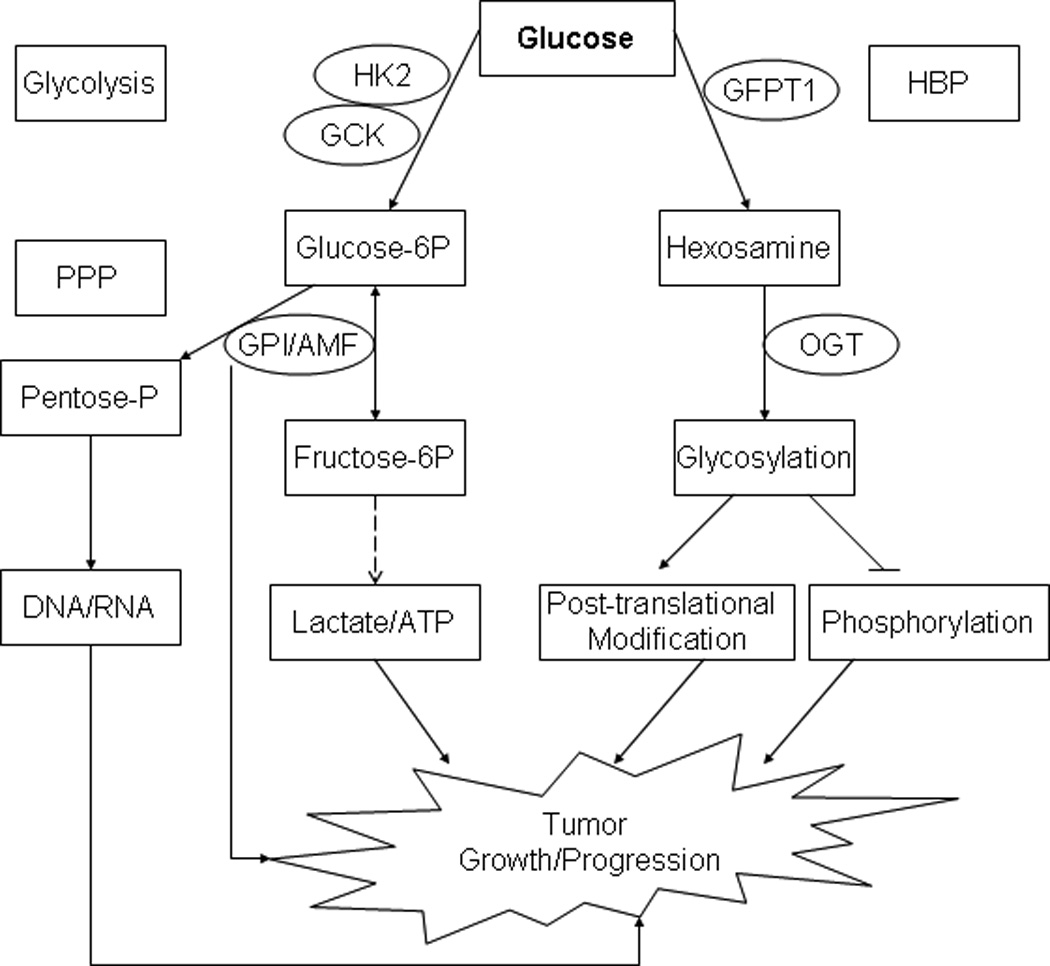
Selected glucose metabolic genes and their potential roles in tumor development. PPP: pentose phosphate pathway. Hexokinases (HK) 2 and GCK/HK4 phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate (Glucose-6P), the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways including glycolysis 25. GPI (phosphoglucose isomerase) catalyzes the reversible isomerization of Glucose-6P and fructose-6P, and guide the glucose flow to the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) 28. GPI also functions as an autocrine motility factor (AMF), secreted from the tumor cells to promote progression 29. GFPT1 is the first and rate-limiting enzyme of the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP) and controls the flux of glucose into the hexosamine pathway. OGT is a glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the addition of a single N-acetylglucosamine in O-glycosidic linkage to serine or threonine residues. O-linked glycosylation plays a role in controlling gene expression, fuel metabolism, cell growth, differentiation, and cytoskeleton organization 30.
