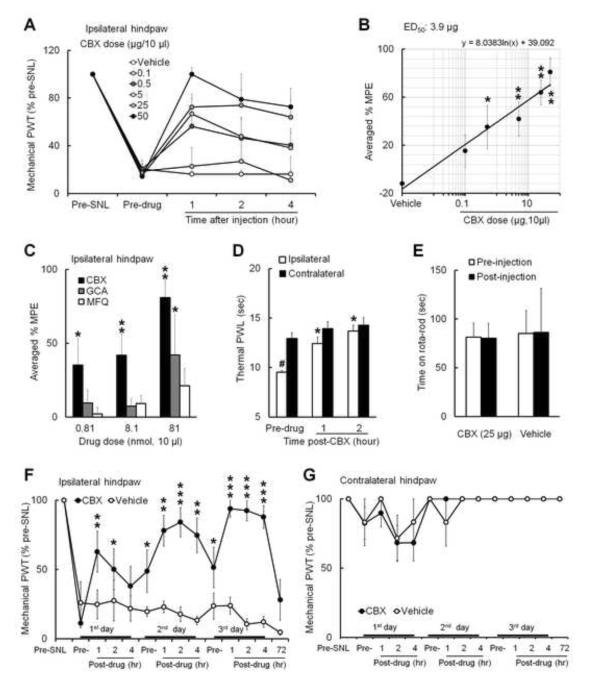
Fig. 1. Intrathecal injection of carbenoxolone inhibits mechanical and heat hypersensitivity in nerve-injured rats.
(A) At 2–3 weeks after an L5 spinal nerve ligation (SNL), intrathecal injection of carbenoxolone (CBX, 0.1 μg: n=5; 0.5 μg: n=6; 5 μg: n=7; 25 μg: n=8; 50 μg: n=5; vehicle: n=6, 10 μl) dose-dependently increased ipsilateral paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) of rats from pre-drug value, reflecting attenuated mechanical hypersensitivity. (B) The dose-response function of CBX-induced inhibition of mechanical hypersensitivity was established based on the averaged % MPE at 1, 2, and 4 h after drug injection. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 versus vehicle, one-way ANOVA. (C) The averaged % MPEs of the same molar doses of intrathecal CBX (0.5 μg/0.81 nmol, 5 μg/8.1 nmol, 50 μg/81 nmol, 10 μl), glycyrrhizic acid (GCA, 0.81 nmol: n=6; 8.1 nmol: n=5, 81 nmol: n=5) and mefloquine hydrochloride (MFQ, 0.81 nmol: n=5; 8.1 nmol: n=5, 81 nmol: n=6) on inhibiting mechanical hypersensitivity. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 versus vehicle, two-way ANOVA. (D) The ipsilateral paw withdrawal latency (PWL) to heat stimuli was shorter than that on the contralateral side (n=6), reflecting heat hypersensitivity in ipsilateral hindpaw. Intrathecal injection of CBX (5 μg) increased ipsilateral PWL from pre-drug level at 1 and 2 h after injection. #p<0.05 versus contralateral side, Student t-test. *p<0.05 versus pre-drug, one-way repeated-measures ANOVA. (E) SNL rats exhibited no motor dysfunction at 1 h post-CBX (25 μg, n=6) or vehicle (saline, n=4) injection. (F) Increase in ipsilateral PWT after repeated intrathecal infusions of CBX (25 μg, 10 μl, n=8, once/day) and not vehicle (n=5) on three consecutive days in rats from day 14 post-SNL. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 versus pre-drug value on first day, two-way mixed model ANOVA. (G) The contralateral PWT was not changed after CBX and vehicle treatment. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.