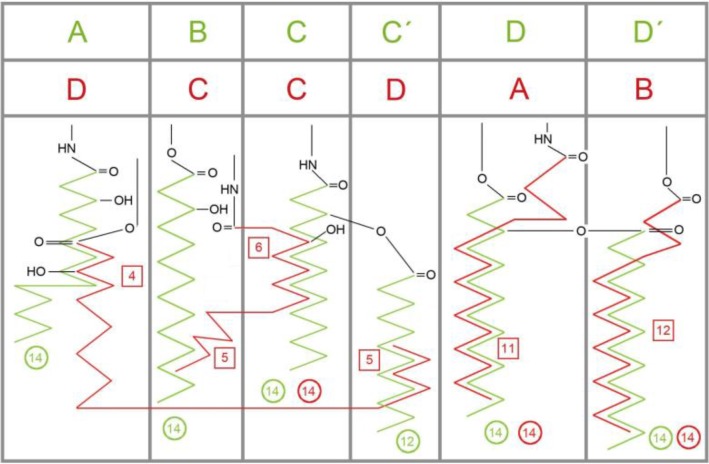
Figure 3.
Schematic display of the rotated (′flipped′) cavity occupation in human MD-2 by acyl side chains of agonistic LPS (green) and antagonistic Lipid IVA (red), found in two crystal structures (PDB codes: 3FXI, 2E59) [18, 32]. Cycles give the chain lengths. For instance, in LPS (green) four chains of (R)-3-hydroxytetradecanoic acid (green circles “14”) are attached to the backbone by either amide or ester bonds in positions A, B, C and D which corresponds to R2′, R2′′, R3′ and R3′′ in an alternative labeling convention [18] and the ′secondary′ lauryl (C12) and myristoyl (C14) and residues are mapped in positions C′and D′, respectively. In Lipid IVA (red) there are only 4 chains, labeled A to D. Its chain D partially occupies the corresponding space of LPS chains A and C′ (green). The square boxes indicate the number of carbon atoms in a chain which are overlapping with an adjacent chain (superposition length). The side chains C and D of antagonists (red) are more deeply buried (see the relative location of the amide and ester head groups).