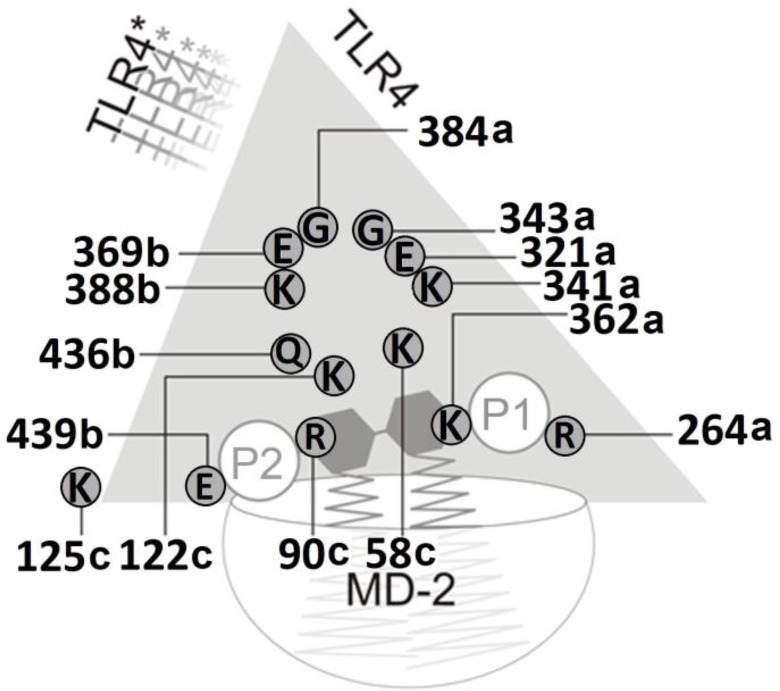
Figure 6.
Schematic view of the computed side chain interactions of the complete human TLR4 ectodomain/MD-2 complex with Lipid IVA pointing out the receptor antagonistic action of Lipid IVA in the human system. Note the inverted (flipped) orientation of the sugar-phosphate backbone as compared to the agonistic binding of lipid A/LPS to human TLR4/MD-2 as well as to the agonistic interaction of Lipid IVA with murine TLR4/MD-2 (see Fig. 7). The indicated charged/polar side chains of counter-TLR4* form a “repulsion region” that prevents the association of the TLR4/MD-2/Lipid IVA unit in the human system. As a direct consequence Lipid IVA does not provide the dimerization into an active m-shaped receptor complex in the human system and acts as a competitive inibitor of LPS/lipid A (agonist) binding instead. Counter-subunit TLR4* is leaving or never was in place, which is indicated by the shaded label of TLR4* (upper left side of wedge).