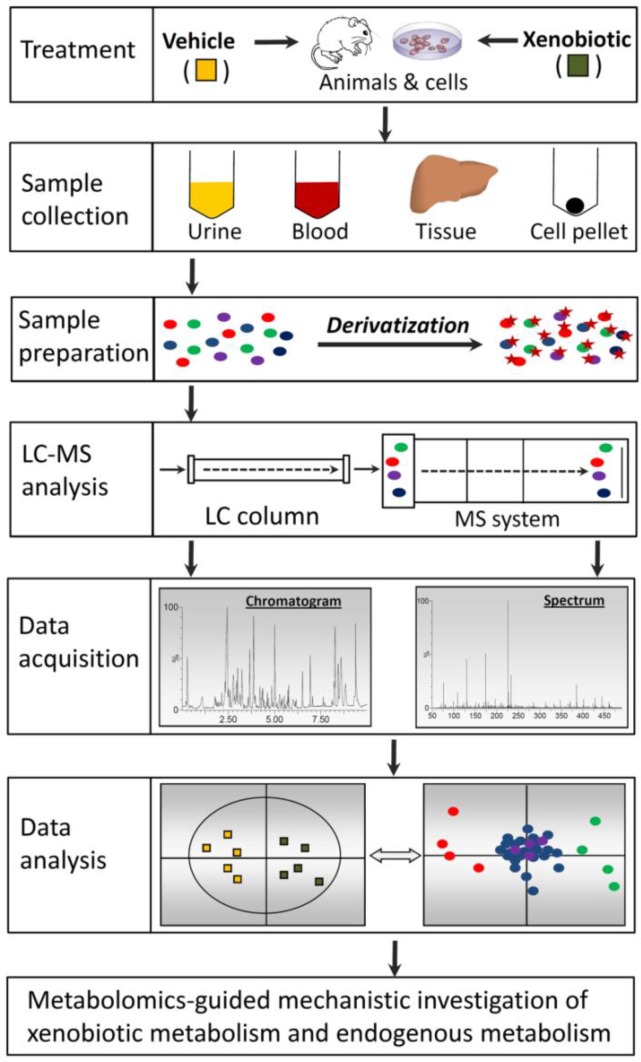
Figure 1.
The work flow of untargeted LC-MS-based metabolomics. Samples from diverse sources need to be processed appropriately to make them compatible with LC-MS analysis. Chemical derivatization can be performed to facilitate the chromatographic separation of metabolites in the LC and increase the sensitivity of metabolite detection in the MS system. Chromatographic and spectral data are acquired by high-resolution LC-MS. Subsequent data processing, such as centroiding, deisotoping, filtering, and peak recognition, yields a data matrix constructed by sample identity, ion identity (RT and m/z), and ion abundance. Through data transformation and multivariate data analysis, a multivariate model can be established in which the scores plot illustrates the principal or latent components of the model as well as sample classification while the loadings plot presents the contribution of each ion to sample classification in the model.