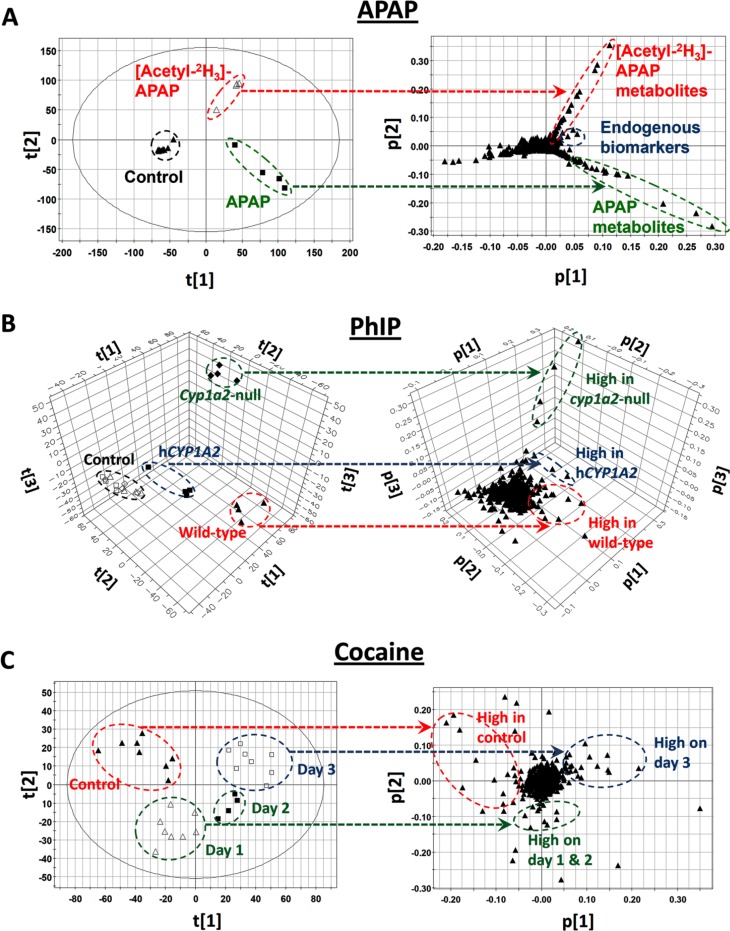
Figure 3.
Examples of LC-MS-based metabolomic investigation of metabolic events in XIT. The dashed arrow lines indicate correlations between samples in the scores plot and ions in the loadings plot of multivariate models. A. Identification of xenobiotic metabolites. Through metabolomic analysis of mouse urine samples from control, APAP, and [Acetyl-2H3]-APAP treatments, the unlabeled APAP and deuterated APAP metabolites can be conveniently identified in the loadings plot. The ions that increased in both APAP and [Acetyl-2H3]-APAP treatments are from endogenous metabolism [53]. B. Role of XME in the biotransformation of xenobiotic. Through the metabolomic analysis of mouse urine samples from PhIP-treated wild-type, Cyp1a2-null, and CYP1A2-humanized mice, genotype-dependent PhIP metabolism is illustrated by the distinctive distribution of PhIP metabolites in the loadings plot [56]. C. Kinetics of xenobiotic-induced changes in endogenous metabolism. Through metabolomic analysis of daily mouse serum samples from a 3-day cocaine treatment, lipid species correlating with development of cocaine-induced hepatotoxicity in mice can be identified in the loadings plot [61].