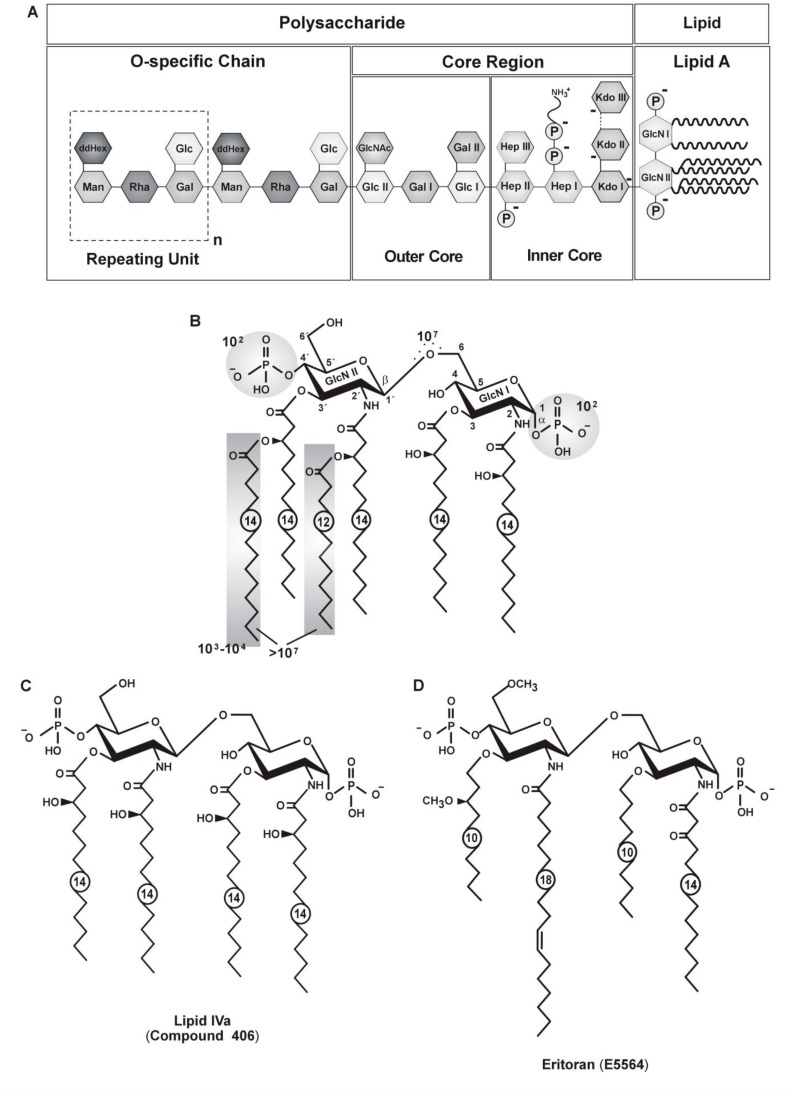
Figure 1.
Structures of a typical enterobacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), lipid A, precursor lipid IVa (compound 406) and Eritoran (E5564). In their general architecture LPS molecules consist of the membrane-anchoring lipid A domain and an oligo- or polysaccharide region of variable length and chemical composition (panel A). The prototypic E.coli Lipid A shows a hydrophobic region composed of six (hydroxy-) acyl chains of 12 and 14 carbon atoms (panel B). In addition, five experimental values of reduction in human monocyte activation due to the lack of the indicated structural elements are given (panel B). The tetra-acylated biosynthetic precursor Lipid IVa of mammalian LPS/lipid A and its synthetic analogue compound 406 are displayed (panel C) next to the tetra-acyl compound Eritoran (E5564) (panel D). See text for details.