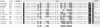Abstract
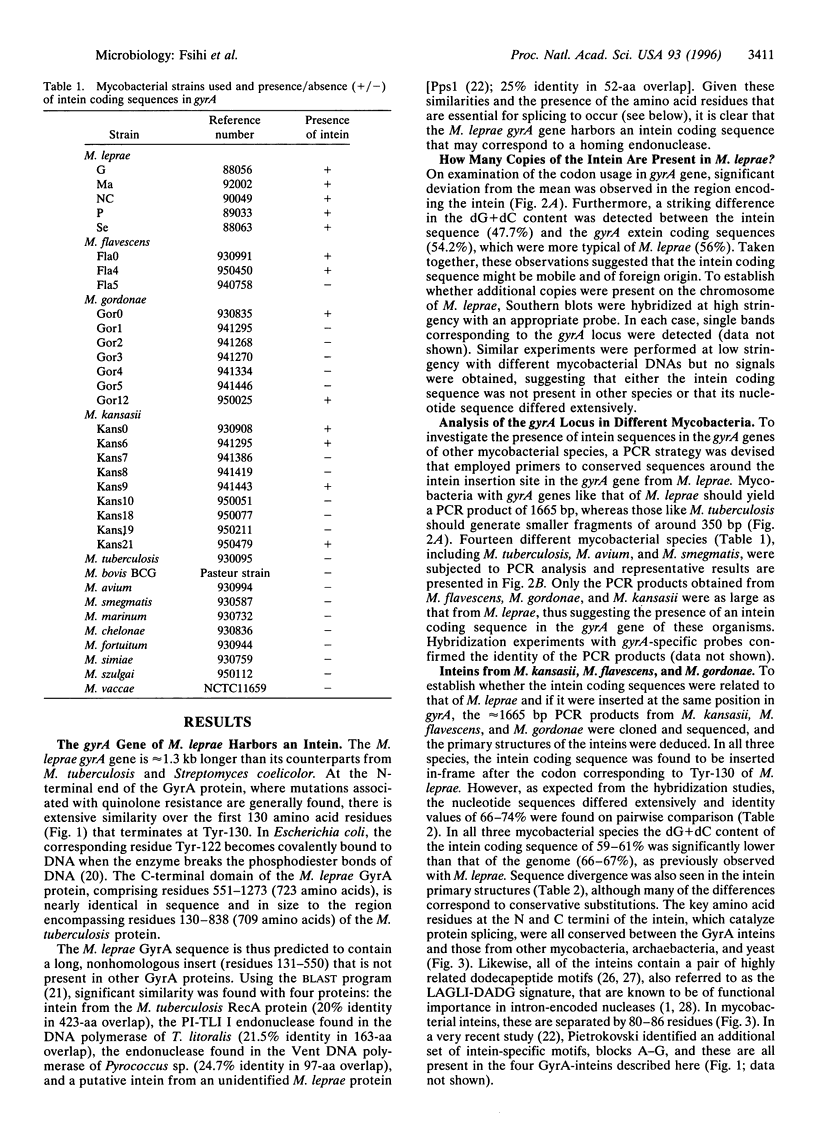
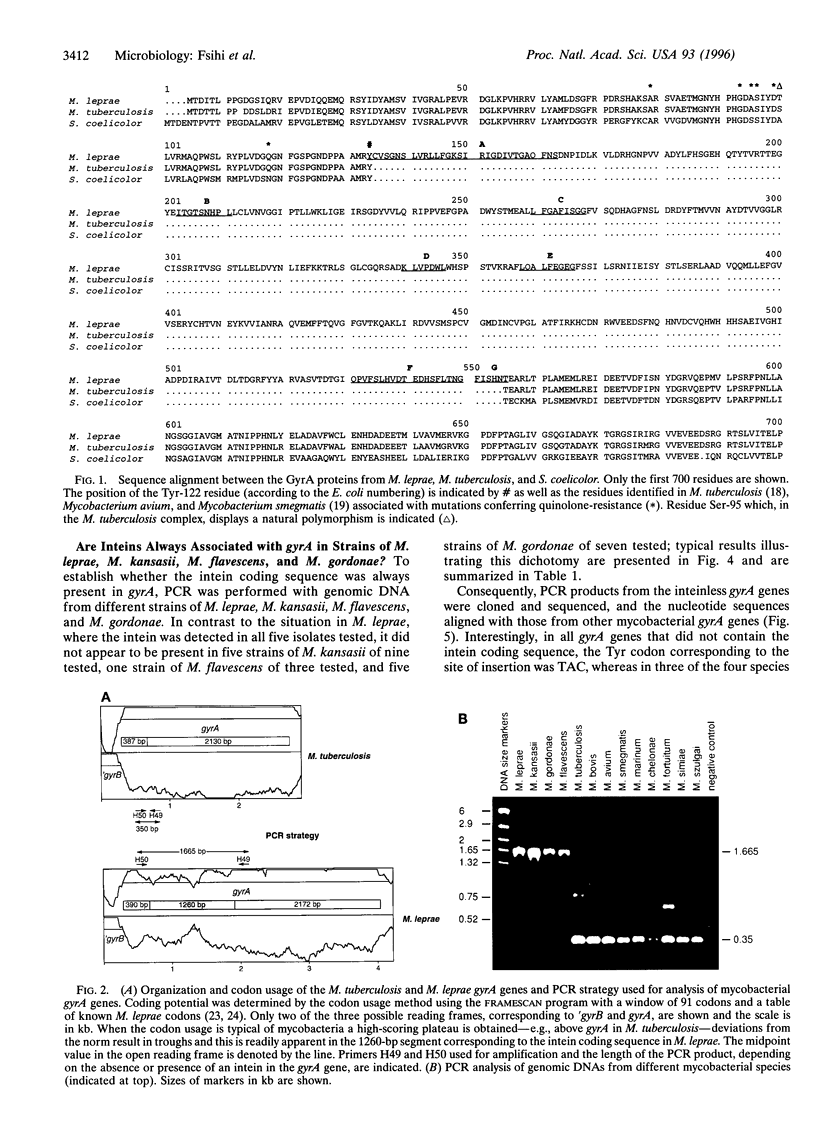
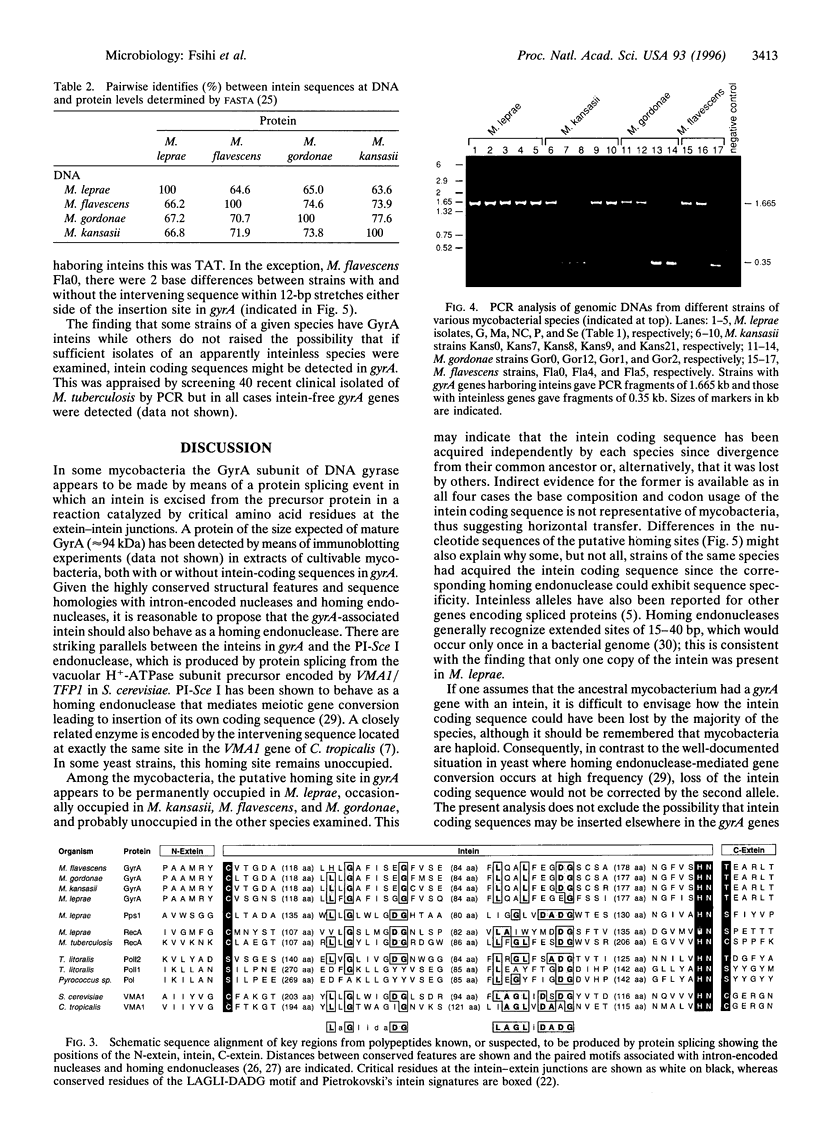
The A subunit of DNA gyrase in Mycobacterium leprae, unlike its counterpart in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is produced by protein splicing as its gene, gyrA, harbors a 1260-bp in-frame insertion encoding an intein, a putative homing endonuclease. Analysis of the gyrA locus from different mycobacterial species revealed the presence of inteins in Mycobacterium flavescens, Mycobacterium gordonae and Mycobacterium kansasii but not in 10 other pathogenic or saprophytic mycobacteria. In all four cases where intein coding sequences were found, they were localized in the same position in gyrA, immediately downstream of the codon for the key active-site residue Tyr-130. The intein products were similar, but not identical, in sequence and the splice junctions displayed all the features found in other polypeptides known to be produced by protein splicing from a precursor protein. Paired motifs, found in homing endonucleases encoded by some group I RNA introns, and inteins showing endonuclease activity, were present in the gyrA inteins as were other intein-specific signatures. Some strains of M. flavescens, M. gordonae, and M. kansasii were shown by PCR analysis to have inteinless gyrA genes, in contrast to the situation in M. leprae where all the isolates possessed insertions in gyrA. Sequencing of the corresponding regions revealed that, although the GyrA protein sequence was conserved, the nucleotide sequences differed in gyrA genes with and without inteins, suggesting that the homing endonuclease displays sequence specificity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambau E., Sougakoff W., Jarlier V. Amplification and nucleotide sequence of the quinolone resistance-determining region in the gyrA gene of mycobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Feb 1;116(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. D. A proposed mechanism for the self-splicing of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11084–11088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colston M. J., Davis E. O. The ins and outs of protein splicing elements. Mol Microbiol. 1994 May;12(3):359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Michel F., McNally K. L. DNA sequence analysis of the 24.5 kilobase pair cytochrome oxidase subunit I mitochondrial gene from Podospora anserina: a gene with sixteen introns. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):381–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00340719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Jenner P. J., Brooks P. C., Colston M. J., Sedgwick S. G. Protein splicing in the maturation of M. tuberculosis recA protein: a mechanism for tolerating a novel class of intervening sequence. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90349-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Sedgwick S. G., Colston M. J. Novel structure of the recA locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis implies processing of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5653–5662. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5653-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Thangaraj H. S., Brooks P. C., Colston M. J. Evidence of selection for protein introns in the recAs of pathogenic mycobacteria. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):699–703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. The comings and goings of homing endonucleases and mobile introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5379–5381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fsihi H., Cole S. T. The Mycobacterium leprae genome: systematic sequence analysis identifies key catabolic enzymes, ATP-dependent transport systems and a novel polA locus associated with genomic variability. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Jun;16(5):909–919. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Thorner J. Homing of a DNA endonuclease gene by meiotic gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):301–306. doi: 10.1038/357301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H. H., Xu J., Gallagher M., Dean G. E. Peptide splicing in the vacuolar ATPase subunit A from Candida tropicalis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7372–7381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata R., Ohsumk Y., Nakano A., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Anraku Y. Molecular structure of a gene, VMA1, encoding the catalytic subunit of H(+)-translocating adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6726–6733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. A., Perler F. B., Noren C. J., Jack W. E. Protein splicing removes intervening sequences in an archaea DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6153–6157. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré N., Bergh S., Chanteau S., Doucet-Populaire F., Eiglmeier K., Garnier T., Georges C., Launois P., Limpaiboon T., Newton S. Nucleotide sequence of the first cosmid from the Mycobacterium leprae genome project: structure and function of the Rif-Str regions. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(2):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Wang J. C. Mapping the active site tyrosine of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5339–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Claisse M., Gargouri A., Kotylak Z., Spyridakis A., Slonimski P. P. Protein encoded by the third intron of cytochrome b gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an mRNA maturase. Analysis of mitochondrial mutants, RNA transcripts proteins and evolutionary relationships. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F. B., Comb D. G., Jack W. E., Moran L. S., Qiang B., Kucera R. B., Benner J., Slatko B. E., Nwankwo D. O., Hempstead S. K. Intervening sequences in an Archaea DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5577–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F. B., Davis E. O., Dean G. E., Gimble F. S., Jack W. E., Neff N., Noren C. J., Thorner J., Belfort M. Protein splicing elements: inteins and exteins--a definition of terms and recommended nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 11;22(7):1125–1127. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.7.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrokovski S. Conserved sequence features of inteins (protein introns) and their use in identifying new inteins and related proteins. Protein Sci. 1994 Dec;3(12):2340–2350. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Goodrich-Blair H. Protein introns: a new home for endonucleases. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90345-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiff H. E., Salazar L., Guerrero C., Philipp W., Huang W. M., Kreiswirth B., Cole S. T., Jacobs W. R., Jr, Telenti A. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis gyrA and gyrB genes and detection of quinolone resistance mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Apr;38(4):773–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.4.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace C. J. The curious case of protein splicing: mechanistic insights suggested by protein semisynthesis. Protein Sci. 1993 May;2(5):697–705. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W., Scazzocchio C., Brown T. A. Internal structure of a mitochondrial intron of Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M. Q., Comb D. G., Paulus H., Noren C. J., Shao Y., Perler F. B. Protein splicing: an analysis of the branched intermediate and its resolution by succinimide formation. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5517–5522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M. Q., Southworth M. W., Mersha F. B., Hornstra L. J., Perler F. B. In vitro protein splicing of purified precursor and the identification of a branched intermediate. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1371–1377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90623-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]