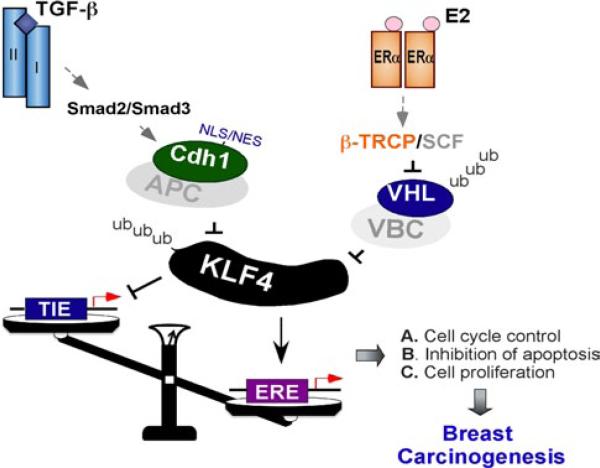
Fig. 3.
KLF4 mediates TGF-β and ER crosstalk. KLF4 is a targeting protein for both TGF-β and ER signaling. As a transcriptional co-factor, KLF4 mediates signaling initiated by TGF-β or estrogen receptors and regulates transactivation responding to TGF-β or estrogen. In epithelial cell, especially in mammary gland epithelial cell, KLF4 acts as a cell growth enhancer, which is regulated by TGF-β and ER signaling. KLF4 is downregulated in response to TGF-β signaling, whereas KLf4 is dramatically upregulated in response to estrogen receptor signaling. Removal of KLF4 in response to TGF-β is governed by E3 ligase APC/CDH1, resulting in the activation of TGF-β-responsive transactivation. In contrary, estrogen receptor signaling shuts down the KLF4 basal turnover that in turn leads to accumulation of KLF4 protein abundance, which is necessary to activate estrogen receptor-mediated transactivation. The basal KLF4 turnover is governed by vHL/vBC E3 ligase. vHL protein stability is regulated by an ubiquitin-proteolytic cascade governed by β-TRCP/SCF