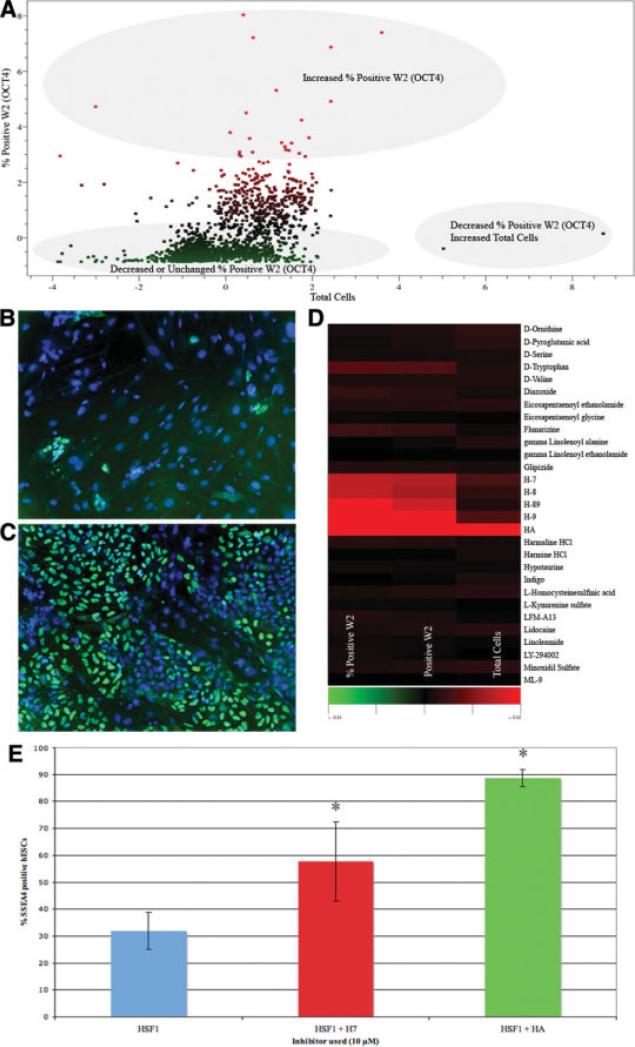
Figure 2.
Data mining reveals small molecule targets that increase OCT4-positive hESCs. (A): Scatter plot from the combined libraries (Biomol and Prestwick) showing targets that increase the percentage of W2 (OCT4)-positive hESCs. (B, C): Control hESCs (B) or hESCs treated with the Rho-kinase inhibitor, HA (C). In the presence of 10 μM HA, there was a dramatic increase in OCT4-positive hESCs as shown by immunofluorescence, with OCT4 in green and nuclei (Hoechst) in blue. (D): Cluster view of a representative Biomol Enzyme plate showing targets that improve hESC growth on the basis of percentage of positive W2 (OCT4). (E): Comparison of HSF1 hESC growth using fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis, using the pluripotency marker, SSEA4, in the presence of 10 μM HA or H7; two hits from the small molecule screen. Treatment with 10 μM HA or H7 resulted in statistically significant numbers of SSEA4-positive hESCs at p ≤ .05. All studies were performed on mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). We have also validated that the H7 and HA small molecules can also promote survival on Matrigel (data not shown), suggesting that these targets can also regulate hESC survival independently of MEFs. Abbreviations: HA, HA-1077; hESC, human embryonic stem cell; SSEA4, stage-specific embryonic antigen 4.