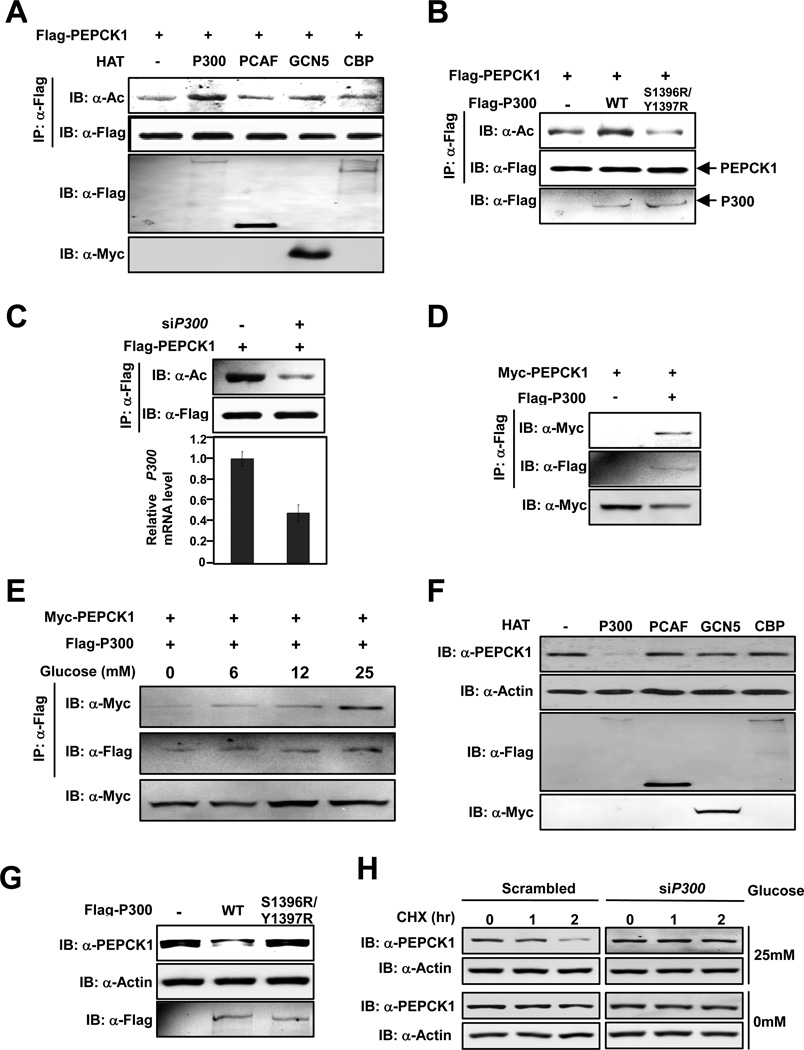
Figure 3. P300 acetylates PEPCK1 and promotes its degradation.
(A) P300 acetylates PEPCK1. Flag-PEPCK1 was co-expressed with different acetyltransferases and purified by Flag beads. Acetylation levels of purified Flag-PEPCK1 proteins were determined. (B) Catalytic activity of P300 is required to acetylate PEPCK1. Acetylation levels of PEPCK1 co-expressed with P300 or its catalytic mutant were determined. (C) P300 knockdown decreases PEPCK1 acetylation level. Acetylation levels of Flag-PEPCK1 expressed and purified from 293T cells with or without P300 knocked down by siRNA were detected. (D) P300 interacts with PEPCK1. Interaction between co-expressed Flag-P300 and Myc-PEPCK1 was detected. (E) P300-PEPCK1 interaction is enhanced by glucose. Interaction between Flag-P300 and Myc-PEPCK1 co-expressed under different concentrations of glucose was determined. (F) P300 overexpression decreases steady state PEPCK1 level. Steady state PEPCK1 levels of 293T cells overexpressing different acetyltransferases were determined. (G) Catalytic activity of P300 is required for decreasing steady state PEPCK1 level. PEPCK1 levels of 293T cells and 293T cells expressing P300 and P300S1396R/Y1397R were determined. (H) P300 is required for PEPCK1 degradation. PEPCK1 degradation rates of Chang’s cells with and without P300 knocked down were measured under both low (0mM) and high (25mM) glucose concentrations. See also Figure S2.