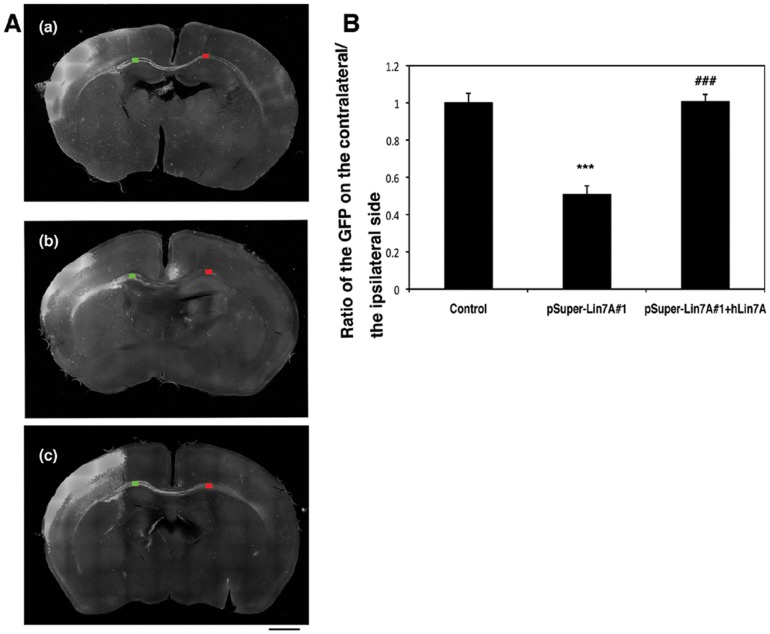
Figure 6. Role of Lin-7A in axon growth ex vivo.
(A), Lin-7A deficiency affects the cortical axon growth. pCAG-EGFP was co-electroporated with (a) control pSUPER vector, (b) pSUPER-mLin7A#1, or (c) pSUPER-mLin7A#1+ hLin-7A into cerebral cortices at E14.5, and fixed at P7. Coronal sections were prepared and immunostained with polyclonal anti-GFP (white). Bar, 1 mm. (B), Quantitative analyses of the ratio of the intensity of GFP-positive axons in the area (green) of Lin-7A-deficient ipsilateral cortex to that in the area (red) of contralateral cortex in A. In the rescue experiments, hLin-7A was co-transfected as an RNAi-resistant version. Values indicate the mean ± S.E.M. n = 3 each. ***P<0.001 vs. Control (Fisher's LSD test); ### P<0.001 vs. Lin7A#1 (Fisher's LSD test).