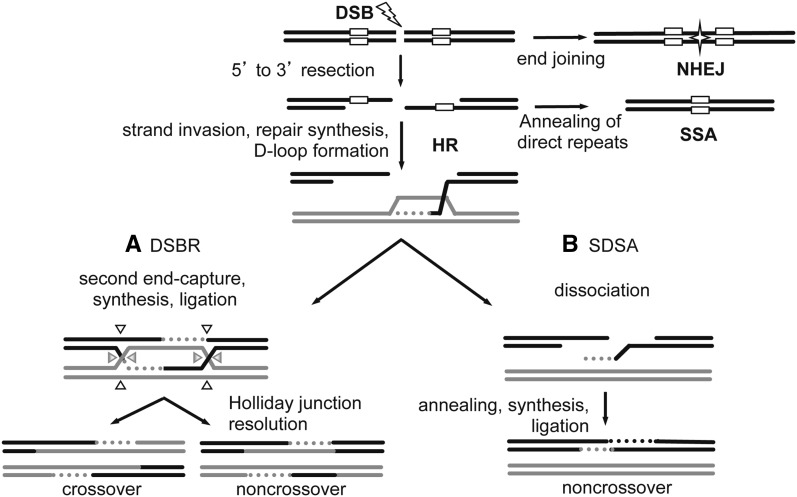
Figure 1.
Models of DSB repair. DSBs can be repaired by homologous recombination (HR), single-strand annealing (SSA) or nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ). In NHEJ, processed ends are joined by ligation (star). HR repair is initiated by 5′ to 3′ resection at the DSB. If the DSB occurs between direct repeats (white boxes), then extensive resection followed by annealing of the direct repeats results in SSA. Otherwise, the resected 3′ overhang invades the homologous template (gray) to initiate repair synthesis (gray dotted line). (A) In the DSBR model, the second strand of the DSB is captured, followed by repair synthesis, and then the newly synthesized strands are ligated to form a double Holliday junction (dHJ). Depending on how the dHJ is cleaved (arrow heads), resolution can result in a crossover or a noncrossover. (B) In SDSA, the newly synthesized strand dissociates, anneals to the other end, the gap is filled in, and nicks are ligated to result in a noncrossover product. The newly synthesized strands in both DSBR and SDSA form heteroduplex DNA (hDNA) between the black and gray sequences. hDNA can be repaired by mismatch repair, resulting in gene conversion (not shown). Direct repeats are shown only for SSA for simplicity.