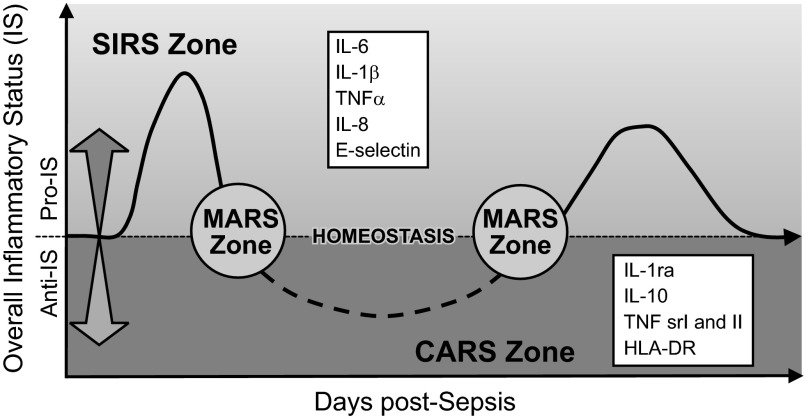
Figure 6.
Concept of the bimodal evolution of the systemic immunoinflammatory response in sepsis. After septic stimulus, there is an immediate and strong shift towards hyperinflammation (SIRS, overall proinflammatory status) defined by an excessive release of the classical proinflammatory cytokines (top box) into the blood. Over time, predominating SIRS gradually subsides and the septic host enters the hypoinflammatory phase (CARS, overall anti-inflammatory status) characterized by a robust release of anti-inflammatory cytokines (bottom box). The temporary transition period between SIRS and CARS zones is defined as MARS and features an approximate balance between the circulating pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators. A septic subject can undergo alternating shifts toward either SIRS or CARS. [Modified from Oberholzer et al. (276), with permission from Lippincott Williams & Wilkens.]