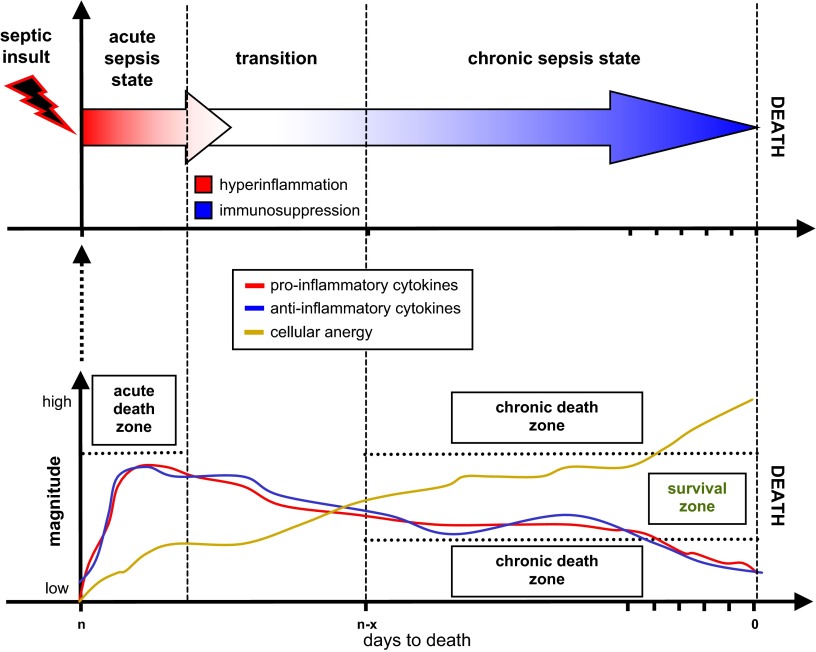
Figure 9.
The immunoinflammatory trajectory in a subject dying from the chronic septic response. The scheme delineates immunoinflammatory fluctuations using the time of death as the reference point given that the time of the sepsis onset in patients is typically unknown. As the severity of sepsis progresses, the magnitude of the systemic pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine response wanes and becomes erratic while the degree of cellular anergy increases. A prelethal immunoinflammatory status of a subject dying from the chronic-type septic response is characterized by a deteriorating but MARS-like cytokine profile (concurrent presence of both pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators in the blood) and robust signs of anergy in the cellular compartment. A chronic inflammatory response (hypoinflammation), although typically associated with late septic deaths, may also occur at an early chronological phase of the disease if a septic host is immunologically unresponsive. The scheme is largely based on data generated in the mouse model of CLP sepsis.