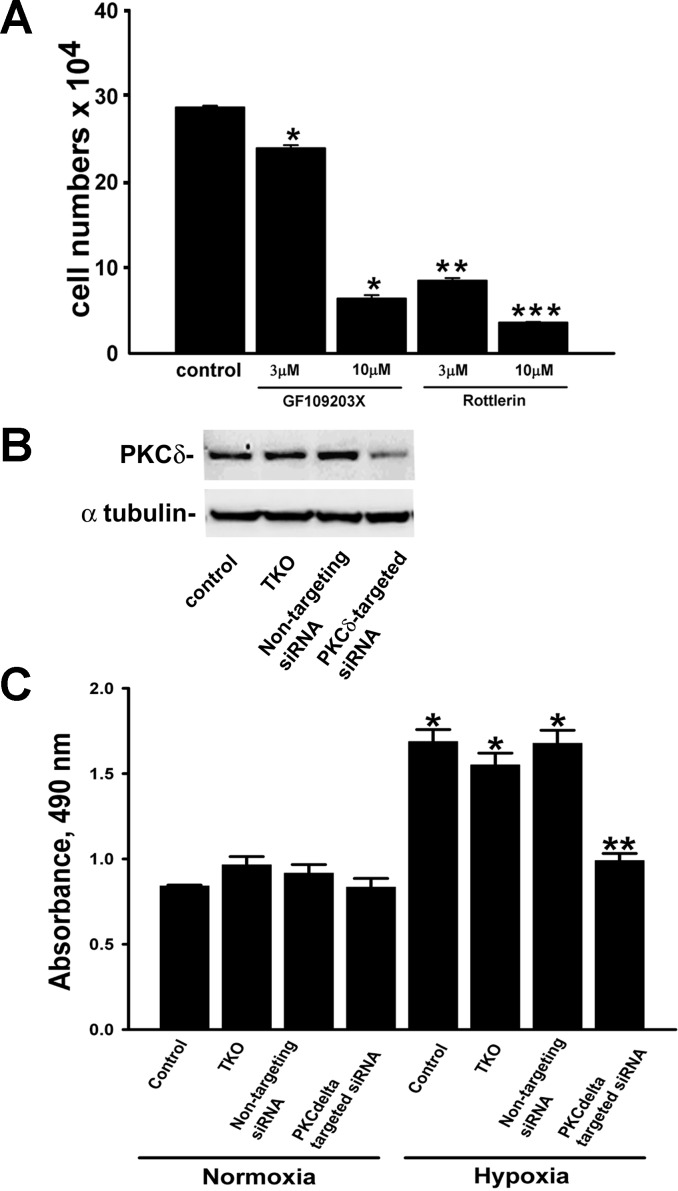
Fig. 2.
Hypoxia-induced proliferation of A549 cells is dependent on PKCδ isozyme. A: maximal inhibition of serum-stimulated growth of A549 cells was achieved in the presence of rottlerin. Cultures received a single treatment with GF109203X or rottlerin. Cells were grown in serum-containing medium for 5 days, trypsinized, and enumerated hemocytometrically. Data are means ± SE from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with control; **P < 0.001, compared with control and GF109203X (3 μM); ***P < 0.001, compared with control and GF109203X (10 μM). B: PKCδ-targeting small interfering (si)RNA selectively reduced PKCδ protein levels in A549 cells as detected by Western immunoblot. Cells were transiently transfected with either PKCδ-targeting siRNA or nontargeting siRNA using TransIT TKO. Cell lysates were collected 48 h posttransfection and immunoblotted for PKCδ and α-tubulin. C: effects of PKCδ siRNA on hypoxia-induced proliferation of A549 cells. Transfected A549 cells were stimulated with either normoxia or hypoxia for 48 h before a mitochondrial activity-based proliferation assay was performed using CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution Reagent. Values are means ± SE of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with normoxia; **P < 0.001, compared with hypoxia control, hypoxic TKO, and hypoxic nontargeting siRNA.