Fig. 4.
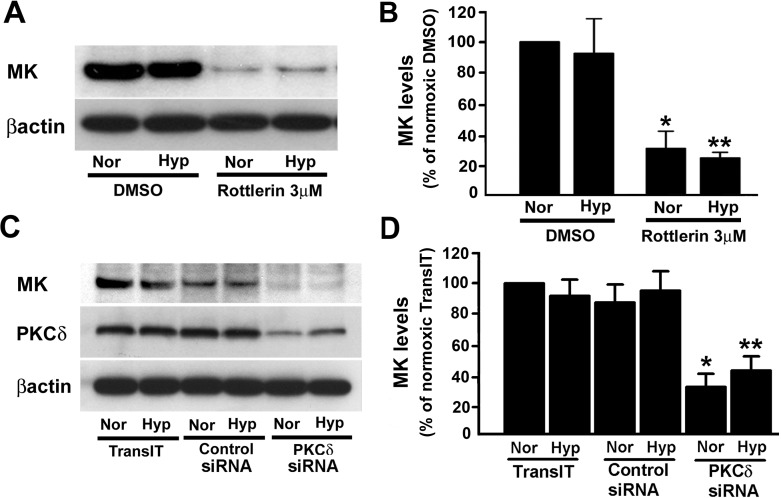
Midkine (MK) expression is regulated by PKCδ. A: treatment with rottlerin results in reduction of MK protein levels in lung epithelial cells. Rottlerin (3 μM) and DMSO, the vehicle, were added to the cells, preincubated at 37°C for 1 h and then exposed to either normoxia (Nor) or hypoxia (Hyp; 1% O2) for 48 h. At the end of the exposure, cells were lysed with lysis buffer and the lysates were used for the determination of MK levels. B: quantification of MK levels from 3 different immunoblots (e.g., Fig. 4A) in control- and rottlerin-treated cells. Values are means ± SE from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, compared with normoxia/DMSO; **P < 0.05, compared with hypoxia/DMSO. C: MK protein levels in A549 cells are attenuated in the presence of PKCδ-targeting siRNA. TransIT-TKO reagent was used to transfect lung epithelial cells with either nontargeting negative control or PKCδ-targeting siRNA. Transfected cells were exposed to either normoxia or hypoxia (1% O2) for 48 h before Western immunoblot analyses for detection of PKCδ, MK, and β-actin. D: Quantification of MK protein levels from 3 different immunoblots (e.g., Fig. 4C) in the presence of PKCδ-targeting siRNA. Values are means ± SE of 3 independent experiments; shown are representative immunoblots. *P < 0.05, compared with control siRNA under normoxia; **P < 0.05, compared with control siRNA under hypoxia.