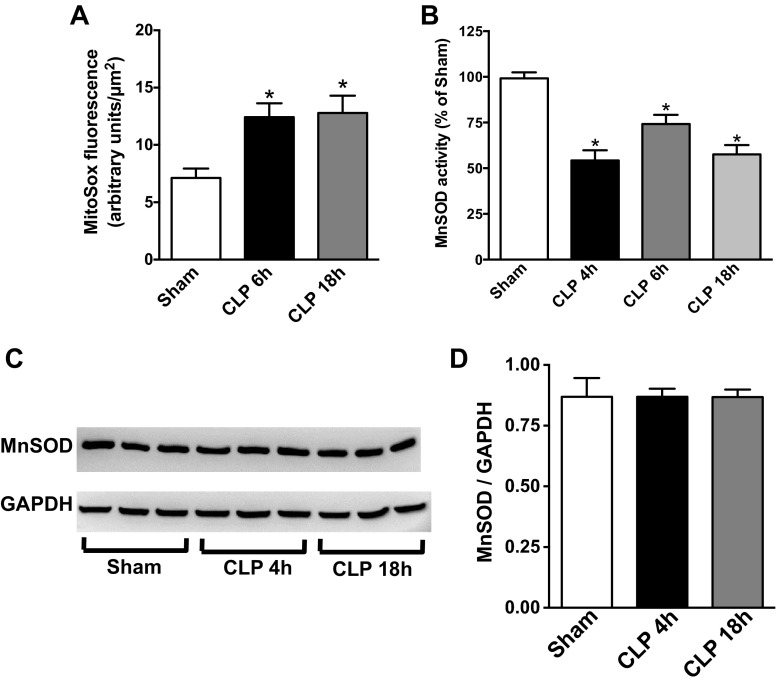
Fig. 2.
Sepsis increased renal mitochondrial superoxide levels and reduced manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) activity. A: renal mitochondrial superoxide levels were measured by MitoSox Red fluorescence using the intravital video microscopy (IVVM) technique (see materials and methods). Values are presented means ± SE, n = 5–9 mice/group. B: renal MnSOD activity was measured at 4, 6, and 18 h post-CLP. Values are expressed as percentage of sham activity (means ± SE, n = 4–8 mice/group). C: representative Western blot showing no change in the expression of MnSOD protein during sepsis. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Image is representative of 3 separate experiments. D: quantification band intensity from C by densitometry. *P < 0.05 compared with Sham.