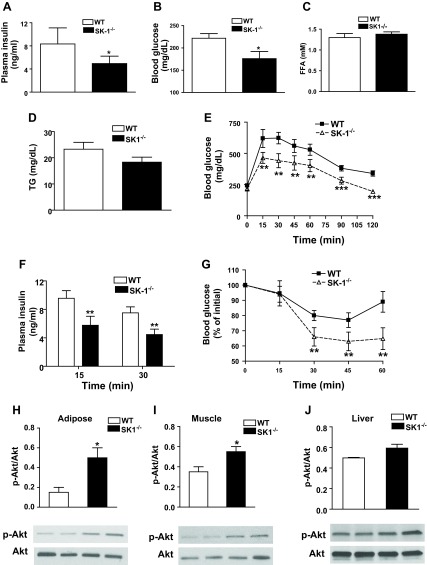
Fig. 6.
SK1 contributes to HFD-mediated glucose tolerance and insulin resistance. Fasting plasma insulin (A), glucose (B), free fatty acids (FFA; C), and triglycerides (TG; D) in male WT and SK1−/− mice fed a HFD for 16 wk. Glucose tolerance test (GTT; E), plasma insulin after GTT (F), and insulin tolerance test (ITT; G) in 16-wk HFD-fed WT and SK1−/− mice. For GTT and ITT, mice were injected ip with either insulin (0.75 U/kg body wt Himulin) or glucose (2 g/kg body wt), and blood glucose was determined at indicated times. For A–G, n = 10 ± SD. Phosphorylated Akt in EAT (H), muscle (I), and liver (J) of HFD-fed WT and SK1−/− mice. For analysis of Akt, mice were fasted for ∼6 h, injected with 0.75 U/kg insulin via the tail vein, and euthanized 10 min later. Tissues were collected for Western blotting using antibodies to phosphorylated Ser473 of Akt and Akt. For H–J, n = 5 ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, WT vs. SK1−/−.