Fig. 3.
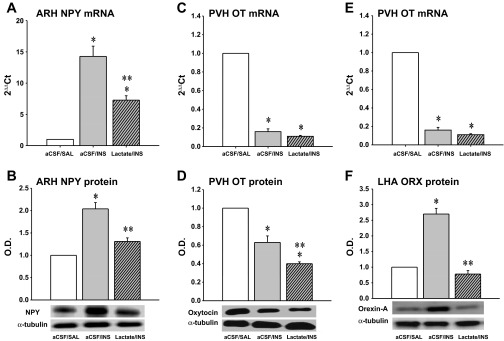
Effects of CV4 l-lactate infusion on hypoglycemia-associated patterns of arcuate nucleus (ARH) neuropeptide Y (NPY), paraventricular (PVH) oxytocin (OT), and lateral hypothalamic area (LHA) orexin (ORX) mRNA and protein expression. The data depict mean ARH NPY, PVH OT, and LHA ORX mRNA (A, B, and C) and normalized protein O.D. levels (C, D, and E) ± SE (n = 5 rats/group) 2 h after treatment with aCSF + SAL, aCSF + INS, or l-lactate + INS. For each animal, micropunches of the ARH, PVN, and LHA were obtained from one side of the hypothalamus in serial 200-μm-thick frozen sections over coordinates intervals of −2.00 to −3.00, −1.30 to −3.20, and −1.30 to −1.70 mm posterior to bregma, respectively, for qPCR analysis of NPY, OT, and ORX mRNA, respectively. Micropunches of these structures collected over identical intervals from the other hemihypothalamus were utilized for neuropeptide and α-tubulin Western blotting. *P < 0.05 vs. aCSF + SAL; **P < 0.05 vs. aCSF + INS. The data show that hypoglycemia increased ARH NPY gene and protein expression; concomitant CV4 lactate infusion only partially reversed this transcriptional response but normalized NPY protein profiles. PVH OT mRNA and neuropeptide levels were both diminished during hypoglycemia; hindbrain lactate repletion did not modify this gene profile but further suppressed OT protein levels. LHA ORX gene and protein expression were decreased or increased, respectively, in response to hypoglycema; lactate infusion to hypoglycemic animals did not alter this transcriptional response but normalized ORX protein production.
