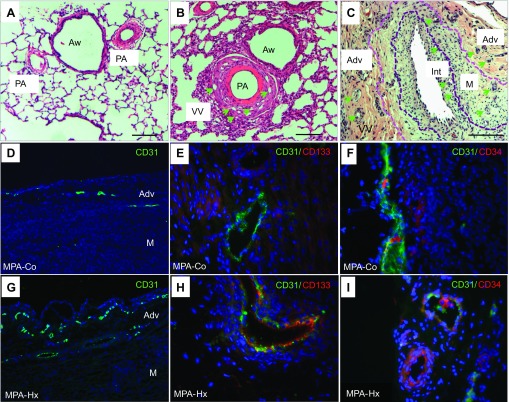
Fig. 1.
Vasa vasorum (VV) neovascularization in pulmonary arteries (PA) of normal and pulmonary hypertensive animals. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung sections of control (A) and hypoxic (B) calves demonstrates that thickening of the PA wall is associated with an apparent increase in the density of VV (green arrows) in vessels from hypoxic animals. Aw, airways; scale bar, 20 μm. In more advanced stages of the pulmonary hypertensive process in the “brisket disease” calf model of PH (see materials and methods), further expansion of VV [in adventitia (Adv), media (M), and even neointima (Int)] is observed (C). Demarcation lines identify the border between the neointimal and medial layers (as defined by the basal elastic lamellae). Scale bar, 100 μm. Immunofluorescence analysis of endothelial and progenitor cell marker expression in main pulmonary artery (MPA) VV shows the expression of CD31+ cells (D and G; ×10 magnification), CD31+CD133+ cells (E and H; ×40 magnification), and CD31+ CD34+ cells (F and I; ×40 magnification) in VV in sections from control (Co) and chronically hypoxic (Hx) animals.