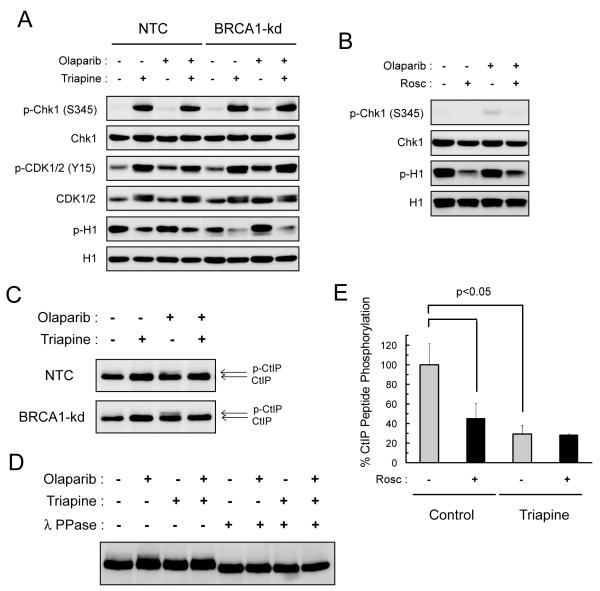
Fig. 4. Triapine inhibits Cdk activity and blocks olaparib-induced CtIP phosphorylation.
A. NTC and BRCA1-kd SKOV-3 cells were treated with 5 μM olaparib, 0.75 μM triapine, or both agents in combination for 24 hr. Total protein was analyzed for the levels of phosphorylated and total Chk1, Cdk1/2, and histone H1 proteins by western blotting. B. NTC SKOV-3 cells were treated with 5 μM olaparib, 20 μM roscovitine (Rosc), or both agents in combination for 24 hr. Total protein was analyzed for the levels of phosphorylated and total Chk1 and histone H1 proteins. C. NTC and BRCA1-kd SKOV-3 cells were treated with 5 μM olaparib, 0.75 μM triapine, or both agents in combination for 24 hr. Total protein was analyzed for CtIP and its phosphorylation-induced band retardation. D. NTC SKOV-3 cells were treated as described in A. Total protein was treated with and without λ protein phosphatase (λ PPase), and then analyzed for CtIP by western blotting. E. NTC SKOV-3 cells were untreated or treated with 0.75 μM triapine for 24 hr. Total native protein was prepared for immunoprecipitation with an anti-CDK2 antibody. In vitro kinase reactions were performed with immunoprecipitated CDK2 and the CtIP peptide substrate in the presence or absence of 10 μM roscovitine. Levels of phosphorylation were measured by the ADP-Glo kinase assay to determine % CtIP peptide phosphorylation. Data are means ± SD.